by Calculated Risk on 2/08/2022 11:13:00 AM
Tuesday, February 08, 2022
NY Fed Q4 Report: Total Household Debt Increases to $15.6 trillion
From the NY Fed: Robust Mortgage and Auto Loan Originations Help Drive Total Household Debt to $15.58 Trillion in Q4 2021
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York's Center for Microeconomic Data today issued its Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit. The Report shows that total household debt increased by $333 billion (2.2%) to $15.58 trillion in the fourth quarter of 2021. The total debt balance reflects an increase of $1 trillion during 2021 and is $1.4 trillion higher than at the end of 2019. In nominal terms, the 2021 total increase in overall debt is the largest seen since 2007. The Report is based on data from the New York Fed's nationally representative Consumer Credit Panel.
Mortgage balances rose by $258 billion in the fourth quarter of 2021 and stood at $10.93 trillion at the end of December. Credit card balances increased by $52 billion, representing the largest quarterly increase observed in the 22-year history of the data. However, credit card balances remain $71 billion lower than at the end of 2019. Auto loan balances increased by $15 billion, consistent with the previous two quarters. Student loan balances contracted by $8 billion, remaining roughly flat in nominal terms at the end of 2021 after almost two decades of steady increases. In total, non-housing balances grew by $74 billion.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Here are three graphs from the report:
The first graph shows aggregate consumer debt increased in Q4. Household debt previously peaked in 2008 and bottomed in Q3 2013. Unlike following the great recession, there wasn't a huge decline in debt during the pandemic.
From the NY Fed:
Aggregate household debt balances increased by $333 billion in the fourth quarter of 2021, a 2.2% rise from 2021Q3, and the largest increase since 2007 in both percentage and nominal terms. Balances now stand at $15.58 trillion, reflecting an increase of $1 trillion during 2021, and stand $1.4 trillion higher than at the end of 2019.
 The second graph shows the percent of debt in delinquency.
The second graph shows the percent of debt in delinquency.The overall delinquency rate was unchange in Q4. From the NY Fed:
Aggregate delinquency rates were flat in the fourth quarter of 2021 but remain very low, after declining sharply through the beginning of the pandemic. The fourth quarter saw a continued decline in late delinquency offset by a small increase in the share of earlier delinquency. The low delinquency rates have reflected forbearances (provided by both the CARES Act and voluntarily offered by lenders), which protect borrowers’ credit records from the reporting of skipped or deferred payments but are now winding down. As of late December, 2.7% of outstanding debt was in some stage of delinquency, a 2.0 percentage point decrease from the fourth quarter of 2019, just before the COVID-19 pandemic hit the United States. Of the $424 billion of debt that is delinquent, $298 billion is seriously delinquent (at least 90 days late or “severely derogatory”, which includes some debts that have been removed from lenders’ books but upon which they continue to attempt collection).
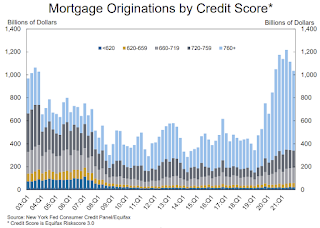 The third graph shows Mortgage Originations by Credit Score.
The third graph shows Mortgage Originations by Credit Score.From the NY Fed:
The credit scores of newly originated mortgages had increased in the early part of the pandemic, but have declined in recent quarters, yet remain very high and reflect a continuing high quality of newly opened mortgages as well as a higher share of refinances. The median credit score on newly originated auto loans was roughly flat. ... In all, 2021 saw historically high volumes of new extensions of installment credit for both mortgages and auto loans. Mortgage originations, measured as appearances of new mortgage balances on consumer credit reports and which include refinances, were at $1 trillion in 2021Q4. In annual terms, mortgage origination volumes were at a historic high in 2021, with over $4.5 trillion in mortgages originated.There is much more in the report.


