by Calculated Risk on 10/08/2006 12:25:00 AM
Sunday, October 08, 2006
Homebuilder Hovnanian to cut jobs
From the Star Ledger: Housing slide prompts Hovnanian to cut jobs
In an internal memo to employees dated Oct. 3, Chief Executive Ara K. Hovnanian said an unspecified number of staff reductions were necessary in order "to remain healthy," as the nation's eighth-largest U.S. home builder grapples with the broad downturn plaguing its industry.Paper-money has posted the Hovnanian internal memo:

MEMORANDUM TO: All Associates
FROM: Ara K. Hovnanian
DATE: October 3, 2006
A few months ago I wrote to you about the changing market conditions in our industry and our concerns about how long the downturn in homebuilding may last. Since that time, the market has slowed further still, representing one of the steepest declines in new home sales in our memory. Most of our markets have been affected, some severely. At this point, we are preparing for a long period of slower sales, at least through 2007 and perhaps beyond.
...
The most difficult adjustment we have had to make to the changing market is in the area of staffing. In many locations, including corporate headquarters, we have been forced to face the fact that we no longer have enough work for all of our Associates. ...
emphasis added
Friday, October 06, 2006
Greenspan: Worst may be over for Housing
by Calculated Risk on 10/06/2006 06:08:00 PM
Bloomberg reports: 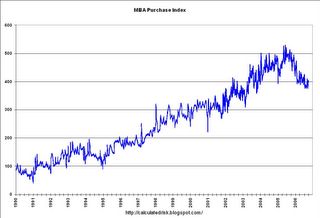
Former Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan said the "worst may well be over" for the U.S. housing industry that's suffering its worst downturn in more than a decade.The graph shows the MBA Purchase Index since it's inception in 1990. On a long term scale, I don't see any significant "flattening out".
Greenspan, speaking at a conference in Calgary today, pointed to a "flattening out" of weekly mortgage applications after they went down "very dramatically."
Housing: Demolitions and Other Losses
by Calculated Risk on 10/06/2006 02:43:00 PM
UPDATE: This is part of a series, and there were several important caveats in the first post. From the first post, Demographics and Housing Demand
I'm trying to answer one of the key housing questions: How far will New Home sales fall? This is a complicated question and, of course, the quantity demanded depends on the price - and homebuilders are already responding to the sluggish market by lowering their prices and / or offering incentives. So how quickly prices fall is a key determinate on how far New Home Sales decline.This post:
... This is a look at the national market. Note that demographic drivers in local markets will differ considerable from the national trends. As an example the population in Detroit is declining, and since housing is very durable, prices for existing homes are below replacement costs.
In the previous post, based on current demographics, I calculated that the U.S. housing stock would need to increase by 1.2 million units per year - all else being equal. A couple of people noted that the number of new units needed would then be 1.2 million plus the number of units lost each year (through demolition or other losses).
In the comments, mort-fin recommended a paper by Eggers & Moumen: Components of Inventory Change: 2001-2003. From their paper:
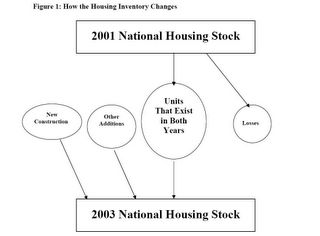 Click on figure for larger image.
Click on figure for larger image. In the context of Figure 1, the Census Bureau provides estimates for both rectangles (the 2001 and 2003 housing stocks) and one oval (units added through new construction between 2001 and 2003). No one estimates the other three ovals: the number of units that belong to both the 2001 and 2003 housing stock, units lost to the housing stock between 2001 and 2003, and other additions to the housing stock between 2001 and 2003.The paper has a detailed analysis of the housing market from 2001 to 2003. A fairly large number of housing units are taken out of service each year (mobile homes moved, units changed to nonresidential use, etc.) and a similarly large number is added back in each year (changed to residential use, returned to service after temporary loss, etc.).
While losses and other additions are small relative to the overall stock, they encompass important features of how housing markets evolve. ... Losses can be either permanent or temporary. Units destroyed by natural disasters or intentionally demolished are permanent losses. Temporary losses include units that are merged into other units or units that are used for nonresidential purposes. Additions can include units resulting from splitting up larger units, mobile home move-ins, and units that had been used formerly for nonresidential purposes.
Demolitions
The number of units lost to demolitions and disasters, from 2001 to 2003, was 382,000, or about 191,000 per year.
However there is a basic problem applying this analysis to the current market. Many demolitions and temporary losses are voluntary and are dependent on market conditions.
As an example there have been 8 units demolished on my block during the last four years. All of these units have been replaced, or are in the process of being replaced, with new construction. A similar construction boom occurred during the late '80s, but not a single unit was demolished and replaced during the previous housing bust from 1990 to 1996.
During boom times, many more units are removed from stock by demolitions temporarily reducing the overall housing stock. This actually puts some upwards price pressure on homes!
Back to my block: there were an additional four units scheduled for demolition this year. The builders have put off their plans and are now leasing out the existing properties. Note: Yes, it feels like I live in a construction zone. Welcome to a Southern California beach community during a housing boom.
I suspect this is happening everywhere; small builders are delaying projects if they don't already have a shovel in the ground. So the number of demolitions over the next couple of years will probably be substantially below the levels of the last few years (and below the 2001 to 2003 period in the Eggers & Moumen study).
So a demographics analysis would suggest 1.2 million new units are needed per year. During the 2001 to 2003 period, an additional 190 thousand new units were needed per year due to demolitions - but that number will be lower during the bust. Also, the 1.2 million figure is reduced by the number of new mobile homes added each year (147K according to Bill Conerly in the comments to the previous post).
So maybe an estimate of 1.4 million units per year would be generous. This number would then be reduced by the overhang of excessive building of the last few years. More to come ...
September Employment Report
by Calculated Risk on 10/06/2006 10:17:00 AM
The BLS reports: U.S. nonfarm payrolls climbed by 51,000 in September, after a revised 188,000 gain in August, and the unemployment rate fell slightly to 4.6% in September from 4.7% in August. Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
Here is the cumulative nonfarm job growth for Bush's 2nd term. The gray area represents the expected job growth (from 6 million to 10 million jobs over the four year term). Job growth is about in the middle of the expected range.
The following two graphs are the areas I've been watching closely: residential construction and retail employment.
Residential construction employment decreased by 15,100 jobs in September and is down 54.1 thousand, or about 1.6%, from the peak in February. This is the beginning of the loss of several hundred thousand residential construction jobs over the next year or so.
Note the scale doesn't start from zero: this is to better show the change in employment.
Retail employment declined 11,900 jobs in September. The YoY change in retail employment is now -0.5%.
The YoY decrease in retail employment is concerning: see Retail Employment
It appears the expected job losses in residential construction employment has started. I expect the rate of losses to pick up in the coming months. Overall, the upwards revision to the August report offset the weak September report.
Thursday, October 05, 2006
Fed's Kohn on Housing
by Calculated Risk on 10/05/2006 02:13:00 PM
Fed Vice Chairman Donald L. Kohn spoke yesterday on the U.S. Economic Outlook. Kohn made several comments regarding housing that are worth reviewing. I'm going to jump around, so please read the speech for his complete comments.
First, Dr. Kohn focused on housing starts as a metric to discuss the housing market. Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
Here is a graph of housing starts since Jan 1959; the beginning of the data series from the Census Bureau. From Dr. Kohn:
"From a trough of fewer than 1.5 million units at an annual rate during the recession of 2000, starts of new single-family and multifamily homes rose to a post-World War II high of 2.2 million units last year."Kohn's recent numbers are correct, but it might be interesting to understand why Kohn is wrong about previous periods. Demographics for housing were actually more favorable in the '70s and '80s than today.
 The second chart shows the trend of people per housing unit in the United States. The number of persons per unit was trending down until around 1990 and then flattened out. There was a rapid decrease in the '70s as the boomers started forming new households en masse. The reason for the record starts in the '70s was due mostly because of the shift in the number of people per housing unit. See the following table:
The second chart shows the trend of people per housing unit in the United States. The number of persons per unit was trending down until around 1990 and then flattened out. There was a rapid decrease in the '70s as the boomers started forming new households en masse. The reason for the record starts in the '70s was due mostly because of the shift in the number of people per housing unit. See the following table:| Housing Added due to Population Growth and changes in Household Size | |||
| Decade | Due to Population Growth | Due to Change in Household Size | Total Housing Units Added |
| 1940s | 5.84 Million | 2.86 Million | 8.70 Million |
| 1950s | 9.11 | 3.08 | 12.19 |
| 1960s | 8.10 | 2.27 | 10.37 |
| 1970s | 9.05 | 10.65 | 19.70 |
| 1980s | 9.13 | 4.77 | 13.90 |
| 1990s | 13.47 | 0.13 | 13.60 |
| 2000s (through July '06) | 7.63 | 2.04 | 9.67 |
For more on Demographics see this post: Demographics and Housing Demand
More from Kohn:
"... calculations about the sustainable level of housing starts based on demographic factors, such as population growth and household formations, suggest that starts may be closer to their trough than to their peak."As Kohn noted, housing starts peaked at about 2.2 million units per year in 2005. Currently starts are at less than 1.7 million units; a decline of over 0.5 million units at an annualized start rate. So when Kohn says starts are probably closer to the "trough than to their peak", he doesn't think starts will fall to a 1.2 million unit rate.
Here is the math: The Census Bureau projects the population will grow by about 2.85 million people this year. There are approximately 2.4 people per household and this ratio is staying steady. So, all else being equal, the U.S. would need about 1.2 million units per year (edit: new starts would equal 1.2 million plus demolitions). I think Kohn might be optimistic on how far starts will fall, and this doesn't include any potential overhang from overbuilding in 2004 and 2005.
More from Kohn:
"... the fourth quarter of last year seems to provide a reasonable reference point: Since that time, housing starts have fallen about 20 percent, and home sales are down 10 percent. Home-price appreciation has also slowed dramatically since late last year, and some local markets have experienced outright price declines. Homebuilders report that cancellations have increased sharply, especially for second homes. Realtors note that existing houses are staying on the market longer, and sellers must increasingly make concessions to buyers."Reported New Home sales are off 18% from the Q4 2005 to the three most recent months. Existing Home sales are off about 12% from the peak of 2005. So I think Kohn is underestimating the decline in sales so far. And when cancellations are considered, the picture is even more bleak.
In the previous post I agreed with Kohn's assertion:
"To date there is little evidence that this correction in the housing market has had any significant adverse spillover effects on other parts of the economy."Yes, but so far there have been few BLS reported housing related job losses, and mortgage equity withdrawal (MEW) has been strong. Foreclosures have just started to rise (and rise quickly in some areas), and Kohn completely ignores any impact from the extensive use of nontraditional mortgages.
Kohn seems to be underestimating both the housing bust, underestimating the impact from the loss of jobs and MEW, and overestimating the positive demographics factors. In my view, this leads Kohn to underestimate the future impact of the housing bust on the general economy.
Retail Sales and Initial Unemployment Claims
by Calculated Risk on 10/05/2006 11:37:00 AM
Occasionally I like to look at initial weekly unemployment claims. Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
The Department of Labor announced weekly unemployment claims decreased to 302K last week.
The graph shows the 4 week moving average for unemployment claims. There is still no evidence of a significant slowdown from this data series.
And the AP reports: Retailers Report Strong Gains for September, Aided by Cooler Weather and Falling Gas Prices
Shoppers, encouraged by cooler temperatures and falling gasoline prices, went on a shopping spree in September, giving many retailers better-than-expected gains and lifting the industry's spirits two months before the holiday season. A notable exception was Wal-Mart Stores Inc.Yesterday Fed Vice Chairman Donald Kohn had some comments on the housing market, and he noted:
As retailers reported their results Thursday, the winners crossed many categories, with department stores and teen merchants including Bebe Stores Inc., J.C. Penney Co. Inc. and Federated Department Stores Inc. among the leaders.
"This is a really strong month," said Ken Perkins, president of RetailMetrics LLC, a research firm in Swampscott, Mass. "The back-to-school momentum was strong, weather was really favorable and the big plummet in gasoline prices certainly put more disposable money into consumers' wallets."
Of the first 44 retailers to report September results, 32 topped analysts' expectations and 12 fell short, according to Thomson Financial.
"To date there is little evidence that this correction in the housing market has had any significant adverse spillover effects on other parts of the economy."I agree - so far the impact of the housing bust on the general economy has been minimal. I will post my take on Kohn's housing comments later today.
Wednesday, October 04, 2006
Natural Gas Prices go Negative!
by Calculated Risk on 10/04/2006 10:19:00 PM
The BBC reports: A glut of natural gas supplies in Britain has seen prices collapse and left traders having to pay for it to be taken off their hands. (hat tip: Truck and Barter)
Wholesale gas prices for immediate delivery turned negative on Tuesday as supplies surged in from the new Langeled pipeline from Norway.And for an excellent summary of some other good news from Econbrowser: And they all lived happily ever after
Britain's gas storage capacity is 96% full so firms need to offload supplies.
...
After trading at an average of 26p a therm through September, the spot price for gas delivered immediately fell to -5p during the course of the day, meaning traders are paying to get rid of it.
...
"There is simply too much gas flowing into the UK," said Chris Bowden, chief executive of energy services company Utilyx.
For the opposite view, from Professor Roubini: Some more "good" news about the economy today...and the stock market's delusional "suckers' rally"...
California: Real Estate Agent Boom Continues
by Calculated Risk on 10/04/2006 08:12:00 PM
The California Department of Real Estate reports the total number of Real Estate licensees reached 511,459 in the state at the end of August 2006. This is an increase of 53,000 agents / brokers over the last 12 months. The number of Salesperson licensees has reached 372,199, a 13% increase over one year ago. The number of Broker licensees is 139,260; 8% higher than last year.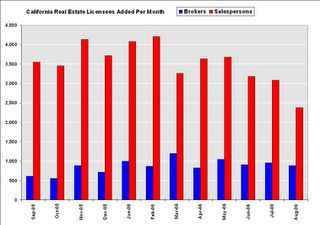 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
This graph shows the number of Brokers and Salespersons licensees added per month in California over the last year. It does appear the number of people obtaining real estate salesperson licenses has slowed, but is still increasing at about 8% per year.
Brokers tend to be more committed to real estate, and the number of new broker licensees added per month has remained steady.
Bernanke: housing slowdown to reduce GDP growth
by Calculated Risk on 10/04/2006 02:08:00 PM
From Reuters: Bernanke--housing slowdown to reduce GDP growth
Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke on Wednesday estimated that the decline in housing construction could reduce gross domestic product growth later this year by a percentage point.The above comments were from the Q&A after Bernanke's speech today. Note that Bernanke believes the payroll tax is a general fund tax and that there is no annual surplus for Social Security:
"I think that I would estimate that slowing housing construction will probably take about a percentage point off of growth in the second half of this year and probably something going into next year as well," the Fed chairman told the Economics Club of Washington at a luncheon here.
At the same time, he said he was unsure how the dynamics of the housing market slowdown would play out, but noted other parts of the economy remain strong, including nonresidential construction.
Although demographic change will affect many aspects of the government’s budget, the most dramatic effects will be seen in the Social Security and Medicare programs, which provide income support and medical care for retirees and which have until now been funded largely on a pay-as-you-go basis.Social Security ran a surplus of $177 Billion in fiscal 2006 alone. I've defended Bernanke before, however this comment is not only inaccurate, but irresponsible.
MBA: Mortgage Applications Rise
by Calculated Risk on 10/04/2006 12:26:00 AM
The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) reports: Mortgage Applications Rise Sharply Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
The Market Composite Index, a measure of mortgage loan application volume, was 633.9, an increase of 11.9 percent on a seasonally adjusted basis from 566.5 one week earlier. On an unadjusted basis, the Index increased 11.5 percent compared with the previous week and was down 10.9 percent compared with the same week one year earlier.Mortgage rates were mixed:
"Refinance applications continue to increase as mortgage rates have declined to their lowest levels since the beginning of the year," said Mike Fratantoni, MBA’s senior director, single family research and economics.
The seasonally-adjusted Refinance Index increased by 17.5 percent to 1970.8 from 1677.5 the previous week and the Purchase Index increased by 7.6 percent to 404.6 from 375.9 one week earlier.
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages increased to 6.24 percent from 6.18 percent ...
The average contract interest rate for one-year ARMs decreased to 5.86 percent from 5.90 percent ...
 The second graph shows the MBA Purchase Index since inception in 1990. The index was started as housing slumped in the early '90s.
The second graph shows the MBA Purchase Index since inception in 1990. The index was started as housing slumped in the early '90s.Note: Actual data after 2001. Before 2001, graph was copied from another source.

This third graph shows the Purchase Index and the 4 and 12 week moving averages since January 2002.
This was the last week of loan activity before the New Nontraditional Mortgage Guidance was released. Refinance and ARM activity was very strong. It will be interesting to see if the guidance has any impact on applications over the next few weeks.
Last 10 Posts
In Memoriam: Doris "Tanta" Dungey
Archive
Econbrowser
Pettis: China Financial Markets
NY Times Upshot
The Big Picture
| Privacy Policy |
| Copyright © 2007 - 2025 CR4RE LLC |
| Excerpts NOT allowed on x.com |


