by Calculated Risk on 4/19/2012 05:16:00 PM
Thursday, April 19, 2012
Homeowner Financial Obligation Ratio near normal, Mortgage obligations still high
From Floyd Norris at the NY Times: Debt Burden Lifting, Consumers Open Wallets a Crack
One measure of the financial health of householders is the level of financial obligations, like required mortgage and credit card payments, to disposable income. By the fall of 2007, those obligations took up 14 percent of disposable income, more than at any time since the Federal Reserve began calculating the statistic in 1980.Norris is referring to the Debt Service Ratio (DSR) from the Federal Reserve.
But now the situation has turned around. The latest figures, for the final quarter of 2011, show that required debt service payments now make up just 10.9 percent of disposable income, the lowest proportion since 1994. A broader measure — which adds in such obligations as property tax and insurance premiums for homeowners, and rent for those who do not own their homes — has fallen to the lowest level since 1984.
There is little mystery in how that happened. First, debt levels have fallen. ... Second, low interest rates mean that servicing that debt costs less. ...
Getting those debt levels down was not a simple matter of making payments, of course. The McKinsey Global Institute estimates that about two-thirds of the reduction came from the cancellation of debt, through write-offs and foreclosures.
I also like to look at the Financial Obligation Ratio (FOR) for homeowners.
Note: This series is useful to look for changes over time, but there are limitations. From the Fed:
The limitations of current sources of data make the calculation of the ratio especially difficult. The ideal data set for such a calculation would have the required payments on every loan held by every household in the United States. Such a data set is not available, and thus the calculated series is only a rough approximation of the current debt service ratio faced by households. Nonetheless, this rough approximation may be useful if, by using the same method and data series over time, it generates a time series that captures the important changes in household debt service payments.
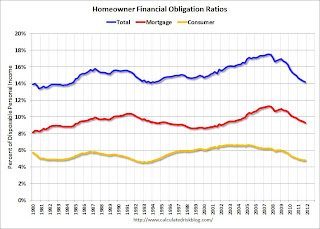 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the Total, Mortgage and Consumer financial obligation ratios for homeowners.
With some decline in debt, and much lower interest rates, the total homeowner financial obligations ratio is back to normal levels. However the mortgage ratio - even with record low mortgage rates - is still somewhat high.
Back in the early '90s, following the previous surge in mortgage obligations, the mortgage ratio declined for about 9 years. For the mortgage ratio to decline further, it would take a combination of more debt reduction and - hopefully - more disposable income.
Philly Fed: "Regional manufacturing activity expanded modestly" in April Survey
by Calculated Risk on 4/19/2012 01:48:00 PM
Earlier from the Philly Fed: April 2012 Business Outlook Survey
The survey’s broadest measure of manufacturing conditions, the diffusion index of current activity, edged down from a reading of 12.5 in March to 8.5. Indexes for new orders and shipments remained positive but were slightly weaker than their March readings. The indexes for new orders and shipments, which decreased about 1 point, remain at relatively low readings.
...
Firms’ responses suggested a notable pickup in levels of employment this
month. The current employment index, which has been positive for eight consecutive months, increased 11 points, to its highest reading in 11 months. ... The average workweek was near steady this month, with 75 percent of the firms surveyed reporting no change in average hours.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Here is a graph comparing the regional Fed surveys and the ISM manufacturing index. The dashed green line is an average of the NY Fed (Empire State) and Philly Fed surveys through April. The ISM and total Fed surveys are through March.
The average of the Empire State and Philly Fed surveys declined in April, and is at the lowest level this year.
Both the NY and Philly Fed surveys indicated expansion in April, at a slower pace than in March, and both were below the consensus forecast. However both surveys showed a strong increase in employment.
Existing Home Sales: Inventory and NSA Sales Graph
by Calculated Risk on 4/19/2012 11:52:00 AM
The NAR reported inventory decreased to 2.37 million in March, down from 2.40 million in February. This is down 21.8% from March 2011, and up 3% from the inventory level in March 2005 (mid-2005 was when inventory started increasing sharply). Inventory was down slightly from March 2004. This decline in inventory has been a significant story over the last year.
Here are some of the reasons for the decline in inventory (mostly a repeat from a post last month):
• The NAR reports active listings, and although there is some variability across the country in what is considered active, most "contingent short sales" are not included. "Contingent short sales" are strange listings since the listings were frequently NEVER on the market (they were listed as contingent), and they hang around for a long time - they are probably more closely related to shadow inventory than active inventory. However when we comparing inventory to 2005, we need to remember there were no "short sale contingent" listings in 2005. However, in the areas I track, the number of "short sale contingent" listings is also down sharply year-over-year.
• There are probably a large number of sellers "waiting for a better market", and we could call this pent-up supply. When the market eventually improves, this pent-up supply will come on the market and probably keep prices from rising - but having less listed inventory now means less downward pressure on prices now.
• There is a seasonal pattern for inventory, and usually December and January have the lowest inventory levels for the year. Although there is some variability, usually inventory increases about 10% to 15% from January to mid-summer. That would put inventory at around 2.55 to 2.7 million by July (up from 2.33 million in January). At the current sales rate, this would push the months-of-supply measure up to 6.8 to 7.2 months from the current 6.3 months. The 1.7% inventory increase from January to March was below the normal seasonal increase of around 8%.
• The number of completed foreclosures declined in 2011 and are expected to increase in 2012. This will probably lead to more REO (lender Real Estate Owned) listed for sale and some increase in the level of inventory.
I don't think this increase will be huge. My guess is that at most this will add 200 thousand listed REOs to the expected seasonal increase that would put listed inventory at 2.75 to 2.9 million in mid-summer - or about 7.4 to 7.8 months-of-supply at the current sales rate. That is higher than normal, but inventory would still be down 10% or more from 2011.
• Tom Lawler has pointed out that there has been a substantial increase in the number of SF homes purchased by investors with the explicit intention to rent the homes out for several years and this is probably another reason for the decline in inventory.
The bottom line is the decline in listed inventory is a big deal, and will take the downward pressure off of house prices. Just like last year, inventory will be something to watch closely all year.
The following graph shows inventory by month since 2004. In 2005 (dark blue columns), inventory kept rising all year - and that was a clear sign that the housing bubble was ending.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
This year (dark red for 2012) inventory is at the lowest level for a March since 2005, and actually slightly below the level in 2004 (not counting contingent sales). Inventory is still elevated - especially with the much lower sales rate.
The following graph shows existing home sales Not Seasonally Adjusted (NSA).
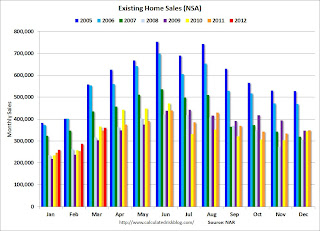 Sales NSA (red column) are above the sales for the 2008, 2009 and 2011 (2010 was higher because of the tax credit). Sales are well below the bubble years of 2005 and 2006.
Sales NSA (red column) are above the sales for the 2008, 2009 and 2011 (2010 was higher because of the tax credit). Sales are well below the bubble years of 2005 and 2006.
It is also important to note that distressed sales were down in March. From the NAR:
Distressed homes – foreclosures and short sales .. – accounted for 29 percent of March sales (18 percent were foreclosures and 11 percent were short sales), compared with 34 percent in February and 40 percent in March 2011.A decline in existing home sales due to fewer distressed sales is a positive for the housing market. Of course distressed sales will probably increase again following the mortgage servicer settlement.
Earlier:
• Existing Home Sales in March: 4.48 million SAAR, 6.3 months of supply
• Existing Home Sales graphs
Existing Home Sales in March: 4.48 million SAAR, 6.3 months of supply
by Calculated Risk on 4/19/2012 10:00:00 AM
The NAR reports: Existing-Home Sales Decline in March but Inventory Down, Prices Stabilizing
Total existing-home sales, which are completed transactions that include single-family homes, townhomes, condominiums and co-ops, declined 2.6 percent to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 4.48 million in March from an upwardly revised 4.60 million in February, but are 5.2 percent above the 4.26 million-unit pace in March 2011.
...
Total housing inventory at the end of March declined 1.3 percent to 2.37 million existing homes available for sale, which represents a 6.3-month supply at the current sales pace, the same as in February. Listed inventory is 21.8 percent below a year ago and well below the record of 4.04 million in July 2007.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows existing home sales, on a Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate (SAAR) basis since 1993.
Sales in March 2012 (4.48 million SAAR) were 2.6% lower than last month, and were 5.2% above the March 2011 rate.
The second graph shows nationwide inventory for existing homes.
 According to the NAR, inventory decreased to 2.37 million in March from 2.40 million in February. Inventory is not seasonally adjusted, and usually inventory increases from the seasonal lows in December and January to the seasonal high in mid-summer.
According to the NAR, inventory decreased to 2.37 million in March from 2.40 million in February. Inventory is not seasonally adjusted, and usually inventory increases from the seasonal lows in December and January to the seasonal high in mid-summer.The last graph shows the year-over-year (YoY) change in reported existing home inventory and months-of-supply. Since inventory is not seasonally adjusted, it really helps to look at the YoY change. Note: Months-of-supply is based on the seasonally adjusted sales and not seasonally adjusted inventory.
 Inventory decreased 21.8% year-over-year in March from March 2011. This is the thirteenth consecutive month with a YoY decrease in inventory.
Inventory decreased 21.8% year-over-year in March from March 2011. This is the thirteenth consecutive month with a YoY decrease in inventory.Months of supply was unchangted at 6.3 months in March.
This was below to expectations of sales of 4.62 million.
Weekly Initial Unemployment Claims at 386,000
by Calculated Risk on 4/19/2012 08:30:00 AM
The DOL reports:
In the week ending April 14, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 386,000, a decrease of 2,000 from the previous week's revised figure of 388,000. The 4-week moving average was 374,750, an increase of 5,500 from the previous week's revised average of 369,250.The previous week was revised up to 388,000 from 380,000. Claims for two weeks ago were revised down.
The following graph shows the 4-week moving average of weekly claims since January 2000.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The dashed line on the graph is the current 4-week average. The four-week average of weekly unemployment claims increased to 374,750.
This is the highest level for the 4-week moving average since January.
And here is a long term graph of weekly claims:

The recent upward increase in claims isn't large, but it is concerning.
Wednesday, April 18, 2012
Some thoughts on housing and foreclosures
by Calculated Risk on 4/18/2012 07:40:00 PM
Some musings ... One of the "givens" for 2012 is that the number of foreclosures will increase following the mortgage servicer settlement agreement. But I've been wondering just how big that increase will be...
A key recent development is the decline in distressed sales; distressed sales are a combination of short sales and lender real estate owned (REO) sales. I've been tracking this for a couple of years, at first just using data for Sacramento, and more recently data for several other cities too (compiled by Tom Lawler). This data shows two important trends: 1) overall distressed sales have been declining, and 2) there has been a shift from REO sales to short sales.
Of course the percent of overall distressed sales could, and probably will, increase soon now that the mortgage settlement agreement has been signed off. But the increase might be less than many people expect. Here are a few reasons:
• According to LPS, there are currently about 2 million properties in the foreclosure process and another 1.7 million loans 90+ delinquent. However many of these loans are in judicial states, and even with the mortgage settlement, it will take some time to work through the courts. So it is hard to imagine a huge wave of foreclosures, if anything it will be more like a sustained high tide in certain judicial foreclosure areas.
• Meanwhile the lenders are offering cash incentives to these same borrowers to do short sales. These incentives are one of the reasons short sales are now at about the same level as REO sales according to LPS. Just yesterday Fannie and Freddie announced new short sale timelines to try to streamline this process further. Sure short sales are still distressed sales, but the impact of short sales on the market is probably less than foreclosures. And more short sales will reduce the number of REOs on the market (listed inventory is what impacts prices).
• Meanwhile the GSEs are trying a new REO-to-rental pilot program, and the regulators are allowing banks to hold REOs as rentals for an extended period. This will probably also reduce the number of REOs hitting the market in the near future. These properties will eventually hit the market, but that is more an argument for why prices will not rise quickly as opposed to prices falling further.
• At the same time, the HARP refinance program is aimed at underwater borrowers who are current on their loan. These borrowers have been making payments for some time, and a new lower mortgage rate will incentivize them to keep paying their mortgage (and also reduce the time until the borrowers have positive equity). This will reduce the pipeline of new delinquencies. HARP is still ramping up, but the number of HARP refinance applications is up sharply according to the MBA.
All and all, I think the number of foreclosures listed for sale might be less than some people expect.
The distressed sales data that I post monthly will probably tell us the size of the wave. But this reminds me a little of the Option ARM issue a few years ago. At first everyone thought there would be a flood of new foreclosures when Option ARMs reset – but over time it became apparent that many borrowers defaulted before the reset, had received a modification, or had refinanced – and there was no flood of reset related defaults.
Last year, for housing, the key was the decline in inventory (something I've been watching closely for the last couple of years). This year inventory is still critical, but any change in the level of distressed sales will be especially important. Just jotting down some thoughts ...
Lawler: Evaluation of Gross Vacancy Rates From the 2010 Census Versus Current Surveys
by Calculated Risk on 4/18/2012 03:42:00 PM
CR note: This is an important topic on trying to understand the number of excess vacant housing units in the US. Unfortunately the various surveys do not match up with the decennial Census data. It appears the vacancy rates in the HVS survey are way too high - yet this is the data most analysts use to estimate the excess number of vacant housing units! In other words, most reported estimates are way too high. The good news is the Census Bureau is trying to understand why ...
From economist Tom Lawler (Lawler identified this issue and pushed for this review):
The Census Bureau posted the following paper presented at the January 2012 meeting of the Federal Committee on Statistical Methodology, and folks interested in the topic should read it.
"Evaluation of Gross Vacancy Rates From the 2010 Census Versus Current Surveys: Early Findings from Comparisons with the 2010 Census and the 2010 ACS 1-Year Estimates" by Arthur R Cresce, Ph. D., Assistant Division Chief for Housing Characteristics, Social, Economic and Housing Statistics Division,
U.S. Census Bureau, SEHSD Working Paper Number 2012-07
Here is an excerpt of the purpose of the paper.
"This paper is part of a larger effort to understand why there are differences in the level of occupied and vacant housing units among the 2010 Census, the 2010 American Community Survey (ACS), the Current Population Survey/Housing Vacancy Survey1 (HVS), and the American Housing Survey2 (AHS). The specific focus of this paper is to provide a snapshot of research completed to date on factors that might explain differences in the level of vacant and occupied housing units between the 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey (ACS). Thus, this paper is not intended to answer all questions or issues concerning these differences. The 2010 ACS 1-year estimate for the gross vacancy rate (GVR) was 13.1 percent compared to 11.4 percent for the 2010 Census. We expect to produce a more comprehensive report on the 2010 Census – ACS differences in 2012 with additional reports to address the differences between the 2010 Census, the HVS and AHS. The goals of these reports are: 1) to understand better why these totals differ and 2) to address particular factors, where possible, that might lead to more consistent results across data collection efforts in the future.”As noted above, this paper focuses on the decennial Census gross vacancy rates and the 2010 ACS gross vacancy rates. The paper notes, however, that Census analysts are also focusing on decennial Census vacancy rates vs. the HVS vacancy rates, as the below excerpt indicates.
“We plan to produce a series of reports in 2012 that will provide a more in depth analysis of potential factors that could explain the reasons for these differences, not only between the ACS and the census, but also among the ACS, the census and the Housing Vacancy Survey. From these reports, we hope to draw conclusions that will enable us, where possible, to take specific actions that could help provide more consistent results between the ACS and the census and, in general, among all our current surveys.”Here are some summary conclusions from the paper.
“1. Although the census and the ACS have different reference periods and different residence rules, we do not believe differences in the reference period and residence rules were major contributors to the overall difference in the gross vacancy rates. However, problems can arise when implementing reference periods combined with residence rules. In the 2010 census, vacant housing units were enumerated in either Nonresponse Followup (NRFU) or in Vacant Delete Check (VDC) which was at least two months after Census Day. This enumeration of the Census Day reference date can make the determination of occupancy status problematic. FRs in the ACS and census enumerators can also misunderstand or misapply a usual residence or current residence rule.Net, the paper suggests that the aggregate ACS vacancy rates for 2010 were probably “too high,” though by how much varied significantly by area/region.
“2. Response categories for occupancy status and vacancy status are similar between the ACS and the 2010 Census, but the way the questions are asked are different. It is not clear, though, if this played a role in explaining some of the differences in classification of housing units.
“3. The 2010 ACS sample was not drawn from the 2010 Census, which may help to explain at least a portion of the difference between the ACS and census GVRs.
“4. Large differences in the reporting of “Other” vacancy status and a possible connection between difficulty in obtaining a response (as measured by percent CAPI in the ACS and “hard-to-count” scores in the census) and differences in the GVR may provide some clues to understanding these differences.
“5. The census implemented coverage improvement procedures, such as special methods to review and confirm the status of housing, which are unique to the census and are not implemented in the ACS. The VDC operation in 2010 resulted in a net decrease of about 537 thousand vacant units.
“6. It was clear from debriefings with interviewers that they faced a very difficult task, Despite common procedures, differences in interpretation of what is an occupied unit can occur, especially in hard to count areas and, in general, in areas experiencing large numbers of foreclosures. Determining the occupancy status of a unit is especially hard in some areas when no household members can be contacted and neighbors are unwilling to provide information. “
Since the Housing Vacancy Survey vacancy rates were well above the ACS vacancy rates, the implication is that the HVS vacancy rates are substantially overstated. However, why the HVS vacancy rates are way too high is still being investigated.
Census currently plans to release the HVS for the first quarter of 2012 at the end of April, though it is not clear why!
Local Home Builder: "Spring selling season is off to a great start"
by Calculated Risk on 4/18/2012 02:19:00 PM
From Jon Lansner at the O.C. Register: O.C. builder Lyon Homes orders soar 89
Builder William Lyon Homes of Newport Beach says it's had a quick business revival as it exited bankruptcy.William Lyon Homes filed for bankruptcy last November, and emerged from bankruptcy in February.
Highlights for Lyon — building in California, Nevada and Arizona — for the three months ended March 31:• New home orders: 321, up 89% vs. a year ago and first 300-plus orders since 2008′s 2nd quarter. (Southern California sales were up 20%.)CEO Gen. William Lyon: "The spring selling season is off to a great start."
• Homes closed: 128, up 15% vs. a year ago.
• Cancellation rate: 9% vs. 15% vs. a year ago.
Note that Lyon builds in California, Arizona and Nevada - all hard hit states.
We've been seeing similar comments from other home builders, but this hasn't shown up yet in the Census Bureau's monthly new home sales report.
AIA: Architecture Billings Index indicates expansion in March
by Calculated Risk on 4/18/2012 10:47:00 AM
Note: This index is a leading indicator for new Commercial Real Estate (CRE) investment.
From AIA: Positive Conditions Persist for Architecture Billings Index
The commercial sector continues to lead the Architecture Billings Index (ABI) which has remained in positive territory for the fifth consecutive month. As a leading economic indicator of construction activity, the ABI reflects the approximate nine to twelve month lag time between architecture billings and construction spending. The American Institute of Architects (AIA) reported the March ABI score was 50.4, following a mark of 51.0 in February. This score reflects a slight increase in demand for design services (any score above 50 indicates an increase in billings). The new projects inquiry index was 56.6, down from mark of 63.4 the previous month.
“We are starting to hear more about improving conditions in the marketplace, with a greater sense of optimism that there will be greater demand for design services,” said AIA Chief Economist, Kermit Baker, PhD, Hon. AIA. “But that is not across the board and there are still a number of architecture firms struggling so progress is likely to be measured in inches rather than miles for the next few months.”
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the Architecture Billings Index since 1996. The index was at 50.4 in March (slight expansion). Anything above 50 indicates expansion in demand for architects' services.
Note: This includes commercial and industrial facilities like hotels and office buildings, multi-family residential, as well as schools, hospitals and other institutions.
According to the AIA, there is an "approximate nine to twelve month lag time between architecture billings and construction spending" on non-residential construction. So this suggests further declines in CRE investment in early 2012, but perhaps stabilizing mid-year.
MBA: Mortgage Applications decrease, Refinance activity increases
by Calculated Risk on 4/18/2012 08:28:00 AM
Form the MBA: Refinance Applications Up, Purchase Applications Down in Latest MBA Weekly Survey
The Refinance Index increased 13.5 percent from the previous week. The seasonally adjusted Purchase Index decreased 11.2 percent from one week earlier.
...
The refinance share of mortgage activity increased to 75.2 percent of total applications from 70.5 percent the previous week.
...
Renewed concerns about sovereign debt in Europe led to a drop in rates last week, with the 30-year rate tying our survey low, reached in early February. Refinance activity picked up in response, increasing 13.5 percent for the week. Participants in our survey indicated that about 32 percent of this refinance volume was for HARP loans," said Jay Brinkmann, MBA's Chief Economist and SVP of Research and Education. "While purchase activity declined sharply for the week, this was mostly due to a 23 percent drop in applications for FHA purchase loans. This drop follows big increases in the demand for FHA loans over several weeks in anticipation of the FHA mortgage insurance premium increases that went into effect last week. This was the largest weekly drop in the government purchase index since the expiration of the first-time homebuyer tax credit in May 2010. The demand for conventional purchase loans was down only slightly."
The average loan size of all loans for home purchase in the US was $233,381 in March 2012, up from $225,463 in February 2012.
...
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages with conforming loan balances ($417,500 or less) decreased to 4.05 percent from 4.10 percent,with points increasing to 0.45 from 0.43 (including the origination fee) for 80 percent loan-to-value ratio (LTV) loans.


