by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2018 12:18:00 PM
Wednesday, January 10, 2018
U.S. Heavy Truck Sales up Year-over-year in 2017
Heavy truck sales increased 3% in 2017 compared to 2016, and heavy truck sales were up 18% year-over-year in December.
First, here is a table of heavy truck sales since 2000 (source: BEA).
Note that sales peaked during the housing bubble, and really collapsed during the great recession. The decline in 2016 was probably related to oil prices.
| Heavy Truck Sales (000s) | |
|---|---|
| Year | Sales |
| 2000 | 461.9 |
| 2001 | 350.1 |
| 2002 | 322.4 |
| 2003 | 328.4 |
| 2004 | 431.6 |
| 2005 | 496.5 |
| 2006 | 544.4 |
| 2007 | 371.1 |
| 2008 | 298.5 |
| 2009 | 199.8 |
| 2010 | 217.6 |
| 2011 | 306.6 |
| 2012 | 346.3 |
| 2013 | 352.6 |
| 2014 | 407.7 |
| 2015 | 449.3 |
| 2016 | 401.0 |
| 2017 | 412.5 |
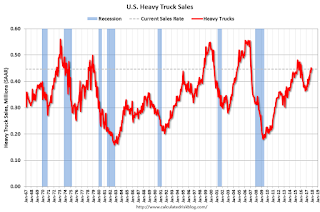
Click on graph for larger image.
This graph shows heavy truck sales since 1967 using data from the BEA. The dashed line is the December 2017 seasonally adjusted annual sales rate (SAAR).
Heavy truck sales really collapsed during the great recession, falling to a low of 181 thousand in April and May 2009, on a seasonally adjusted annual rate basis (SAAR).
Truck sales softened with the decline in oil prices, however with the increase in oil prices over the last year, heavy truck sales increased too.
Heavy truck sales were at 447 thousand SAAR in December 2017, down slightly from 451 thousand in November, and up from 379 thousand in December 2016. With solid construction and rising oil prices, heavy truck sales will probably increase in 2018.
Update: The Inland Empire Bust and Recovery
by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2018 10:09:00 AM
Way back in 2006 I disagreed with some analysts on the outlook for the Inland Empire in California. I wrote:
As the housing bubble unwinds, housing related employment will fall; and fall dramatically in areas like the Inland Empire. The more an area is dependent on housing, the larger the negative impact on the local economy will be.And sure enough, the economies of housing dependent areas like the Inland Empire were devastated during the housing bust. The good news is the Inland Empire is expanding solidly now.
So I think some pundits have it backwards: Instead of a strong local economy keeping housing afloat, I think the bursting housing bubble will significantly impact housing dependent local economies.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the unemployment rate for the Inland Empire (using MSA: Riverside, San Bernardino, Ontario), and also the number of construction jobs as a percent of total employment.
The unemployment rate is falling, and is down to 4.1% (down from 14.4% in 2010). And construction employment is up from the lows (as a percent of total employment), but still well below the bubble years.
So the unemployment rate has fallen to a record low, but the economy isn't as heavily depending on construction. Overall the Inland Empire economy is in much better shape today.
 The second graph shows the number of construction jobs as a percent of total employment for the Inland Empire, all of California, and the entire U.S..
The second graph shows the number of construction jobs as a percent of total employment for the Inland Empire, all of California, and the entire U.S..Clearly the Inland Empire is more dependent on construction than most areas. Construction has picked up as a percent of total employment, but the economy in California and the U.S. is not as dependent on construction as during the bubble years.
MBA: Mortgage Applications Increase in Latest Weekly Survey
by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2018 07:00:00 AM
From the MBA: Mortgage Applications Increase in Latest MBA Weekly Survey
Mortgage applications increased 8.3 percent from one week earlier, according to data from the Mortgage Bankers Association’s (MBA) Weekly Mortgage Applications Survey for the week ending January 5, 2018. This week’s results included an adjustment for the New Year’s holiday. Results for the previous week ending 12/29/17 were revised.
... The Refinance Index increased 11 percent from the previous week. The seasonally adjusted Purchase Index increased 5 percent from one week earlier. The unadjusted Purchase Index increased 44 percent compared with the previous week and was 1 percent lower than the same week one year ago. ...
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages with conforming loan balances ($453,100 or less) increased to 4.23 percent from 4.22 percent, with points decreasing to 0.35 from 0.37 (including the origination fee) for 80 percent loan-to-value ratio (LTV) loans.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph shows the refinance index since 1990.
Refinance activity will not pick up significantly unless mortgage rates fall well below 4%.
 The second graph shows the MBA mortgage purchase index.
The second graph shows the MBA mortgage purchase index. According to the MBA, purchase activity is down 1% year-over-year.
Tuesday, January 09, 2018
Earlier: Small Business Optimism Index Declines in December
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2018 06:40:00 PM
Wednesday:
• At 7:00 AM ET, The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) will release the results for the mortgage purchase applications index.
Earlier from the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB): Average Monthly Optimism Sets All-Time Record in 2017
The Index of Small Business Optimism lost 2.6 points in December, falling to 104.9, still one of the strongest readings in the 45-year history of the NFIB surveys. The highest reading of 108.0 was reached in July 1983, only slightly above November’s 107.5. The lowest reading of 79.7 occurred in April 1980. Two of the 10 Index components posted a gain, five declined, and three were unchanged. The decline left the Index historically strong and maintained a string of exceptional readings that started the day after the 2016 election results were announced. Following the election announcement, the Index rose from 95.0 (a below average reading) for October and pre-election November, to 102.0 in the November weeks after the election, and then to 105.0 in January. This surge in optimism has led to 2017 achieving the highest yearly average Index reading in the survey’s history. The average monthly Index for 2017 was 104.8. The previous record was 104.6, set in 2004.
Job creation was slow in the small-business sector as owners reported a seasonally adjusted average employment change per firm of 0.01 workers. Clearly, a lack of “qualified” workers is impeding the growth in employment. ... Nineteen percent of owners cited the difficulty of finding qualified workers as their Single Most Important Business Problem (up 1 point), second only to taxes. This is the top ranked problem for those in construction (30 percent) and manufacturing (27 percent).
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the small business optimism index since 1986.
The index decreased to 104.9 in December.
Note: Usually small business owners complain about taxes and regulations. However, during the recession, "poor sales" was the top problem. Now labor shortages are moving to the top.
Leading Index for Commercial Real Estate "Ends 2017 on High Note" in December
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2018 05:13:00 PM
Note: This index is possibly a leading indicator for new non-residential Commercial Real Estate (CRE) investment, except manufacturing.
From Dodge Data Analytics: Dodge Momentum Index Ends Year on High Note
The Dodge Momentum Index grew 3.6% in December to 153.9 (2000=100) from the revised November reading of 148.6. The Momentum Index is a monthly measure of the first (or initial) report for nonresidential building projects in planning, which have been shown to lead construction spending for nonresidential buildings by a full year. December’s increase was due to an 8.6% jump in the institutional component of the Momentum Index, while the commercial component eked out a 0.7% gain. For the full year 2017, the Momentum Index averaged 132.3, up 10.7% from the full year average for 2016, with similar improvement for the commercial sector (up 11.4%) and the institutional sector (up 9.7%). After retreating during the third quarter of 2017, the Momentum Index regained its upward track in the fourth quarter, which enabled December’s reading for the Momentum Index to be up 20.9% compared to the same month a year ago. The continued strengthening by the Momentum Index in 2017 suggests that nonresidential building construction activity will advance further during 2018.
emphasis added
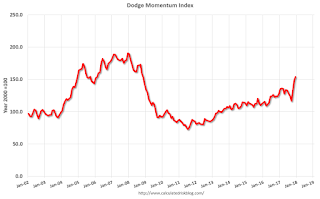 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the Dodge Momentum Index since 2002. The index was at 153.9 in December, up from 148.6 in November.
The index is up 21% year-over-year.
According to Dodge, this index leads "construction spending for nonresidential buildings by a full year". This suggests further growth in 2018.
Fed: Q3 2017 Household Debt Service Ratio Very Low, Starting to Increase
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2018 02:47:00 PM
The Fed's Household Debt Service ratio through Q3 2017 was released on today: Household Debt Service and Financial Obligations Ratios. I used to track this quarterly back in 2005 and 2006 to point out that households were taking on excessive financial obligations.
These ratios show the percent of disposable personal income (DPI) dedicated to debt service (DSR) and financial obligations (FOR) for households. Note: The Fed changed the release in Q3 2013.
The household Debt Service Ratio (DSR) is the ratio of total required household debt payments to total disposable income.This data has limited value in terms of absolute numbers, but is useful in looking at trends. Here is a discussion from the Fed:
The DSR is divided into two parts. The Mortgage DSR is total quarterly required mortgage payments divided by total quarterly disposable personal income. The Consumer DSR is total quarterly scheduled consumer debt payments divided by total quarterly disposable personal income. The Mortgage DSR and the Consumer DSR sum to the DSR.
The limitations of current sources of data make the calculation of the ratio especially difficult. The ideal data set for such a calculation would have the required payments on every loan held by every household in the United States. Such a data set is not available, and thus the calculated series is only an approximation of the debt service ratio faced by households. Nonetheless, this approximation is useful to the extent that, by using the same method and data series over time, it generates a time series that captures the important changes in the household debt service burden.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The graph shows the Total Debt Service Ratio (DSR), and the DSR for mortgages (blue) and consumer debt (yellow).
The overall Debt Service Ratio increased in Q3, and has been moving up slowly from the recent record low. Note: The financial obligation ratio (FOR) also increased in Q3.
The DSR for mortgages (blue) are near the low for the last 35 years. This ratio increased rapidly during the housing bubble, and continued to increase until 2007. With falling interest rates, and less mortgage debt (mostly due to foreclosures), the mortgage ratio has declined significantly.
The consumer debt DSR (yellow) has been increasing for the last five years.
This data suggests aggregate household cash flow has improved significantly since the great recession, but has started to decline slightly recently.
Las Vegas Real Estate in December: Sales Down YoY, Inventory down 36%
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2018 12:47:00 PM
This is a key distressed market to follow since Las Vegas saw the largest price decline, following the housing bubble, of any of the Case-Shiller composite 20 cities.
The Greater Las Vegas Association of Realtors reported Even With Tight Housing Supply, 2017 Was a Strong Year for Local Home Sales; GLVAR Housing Statistics for December 2017
Despite a tight housing supply, the Greater Las Vegas Association of REALTORS® (GLVAR) reported today that 2017 was one of the best years on record for local home sales and that home prices continued to increase from the previous year.1) Overall sales were down year-over-year.
...
By the end of December, GLVAR reported 3,827 single-family homes listed for sale without any sort of offer. That’s down 35.7 percent from one year ago. For condos and townhomes, the 656 properties listed without offers in December represented a 27.9 percent drop from one year ago.
The total number of existing local homes, condos and townhomes sold during December was 3,204. Compared to one year ago, December sales were down 3.5 percent for homes and down 14.8 percent for condos and townhomes.
According to GLVAR, the 46,598 total properties sold during 2017 make it the third best sales year on record and the best year for existing local home sales since 2011. The 2017 sales total exceeds the 41,720 such properties sold in 2016. Last year’s total ranks just below the 47,685 sales recorded in 2009 and the record of 48,798 existing local properties sold in 2011, when prices were bouncing along a post-recession bottom and investors were dominating the market.
...
GLVAR reported that 25.7 percent of all local properties sold in December were purchased with cash, compared to 28.7 percent one year ago. That’s less than half of the February 2013 peak of 59.5 percent, indicating that cash buyers and investors are still active, but playing a smaller role in the local housing market.
At the same time, the number of so-called distressed sales continues to decline. GLVAR said short sales and foreclosures combined accounted for 3.6 percent of all existing local home sales in December, compared to 11 percent of all sales one year ago.
“What a dramatic change from five or six years ago,” Bishop added. “Back then, foreclosures and short sales accounted for about three out of every four homes we sold here in Southern Nevada.”
emphasis added
2) Active inventory (single-family and condos) is down sharply from a year ago.
3) Fewer distressed sales.
BLS: Job Openings "Little changed" in November
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2018 10:07:00 AM
From the BLS: Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary
The number of job openings was little changed at 5.9 million on the last business day of November, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Over the month, hires and separations were little changed at 5.5 million and 5.2 million, respectively. Within separations, the quits rate was unchanged at 2.2 percent and the layoffs and discharges rate was little changed 1.1 percent. ...The following graph shows job openings (yellow line), hires (dark blue), Layoff, Discharges and other (red column), and Quits (light blue column) from the JOLTS.
The number of quits was little changed at 3.2 million in November. The quits rate was 2.2 percent. The number of quits was little changed for total private and increased for government.
emphasis added
This series started in December 2000.
Note: The difference between JOLTS hires and separations is similar to the CES (payroll survey) net jobs headline numbers. This report is for November, the most recent employment report was for December.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Note that hires (dark blue) and total separations (red and light blue columns stacked) are pretty close each month. This is a measure of labor market turnover. When the blue line is above the two stacked columns, the economy is adding net jobs - when it is below the columns, the economy is losing jobs.
Jobs openings decreased in November to 5.879 million from 5.925 in October.
The number of job openings (yellow) are up 4.4% year-over-year.
Quits are up 3.1% year-over-year. These are voluntary separations. (see light blue columns at bottom of graph for trend for "quits").
Job openings are mostly moving sideways at a high level, and quits are increasing year-over-year. This is a solid report.
Monday, January 08, 2018
Tuesday: Job Openings
by Calculated Risk on 1/08/2018 07:02:00 PM
From Matthew Graham at Mortgage News Daily: Mortgage Rates Back Near Recent Highs
Mortgage rates rose today, largely due to bond market movement from the end of last week that never made it onto last week's rate sheets. ... Lenders normally need to see a certain amount of market movement by a certain time of day before issuing mid-day reprices, and Friday's weakness wasn't quite big enough.Tuesday:
All that having been said, the movements in question are small enough that they're mainly affecting closing costs in most cases (as opposed to actual interest rates). As such, most borrowers are still seeing top tier conventional 30yr fixed quotes in the 4.0-4.125% neighborhood. But the closing costs associated with those rates are just about as high as they've been since early 2017.
emphasis added
• At 6:00 AM ET, NFIB Small Business Optimism Index for December.
• At 10:00 AM, Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey for November from the BLS. Jobs openings decreased in October to 5.996 million from 6.177 in September. The number of job openings were up 7.3% year-over-year, and Quits were up 3.3% year-over-year.
Black Knight Mortgage Monitor: New Tax Law Could Impact Home Equity Borrowing
by Calculated Risk on 1/08/2018 03:32:00 PM
Black Knight released their Mortgage Monitor report for November today. According to Black Knight, 4.55% of mortgages were delinquent in November, up from 4.46% in November 2016. The increase was primarily due to the hurricanes. Black Knight also reported that 0.66% of mortgages were in the foreclosure process, down from 0.98% a year ago.
This gives a total of 5.21% delinquent or in foreclosure.
Press Release: Black Knight’s Mortgage Monitor: Tappable Equity at All-Time High, But Tax Code Changes Could Impact Homeowners’ Utilization
Today, the Data & Analytics division of Black Knight, Inc. released its latest Mortgage Monitor Report, based on data as of the end of November 2017. This month, Black Knight finds that tappable equity – the amount of equity available for homeowners to borrow against before reaching a maximum 80 percent total loan-to-value (LTV) ratio – is at an all-time high. However, as Black Knight Data & Analytics Executive Vice President Ben Graboske explained, recent changes to the U.S. tax code may have implications for homeowners’ utilization of that equity.
“As of the end of Q3 2017, 42 million homeowners with a mortgage now have an aggregate of nearly $5.4 trillion in equity available to borrow against,” said Graboske. “That is an all-time high, and up more than $3 trillion since the bottom of the market in 2012. Over 80 percent of all mortgage holders now have available equity to tap, whether via first-lien cash-out refinances or home equity lines of credit (HELOCs). We’ve noted in the past that as interest rates rise from historic lows, HELOCs represented an increasingly attractive option for these homeowners to access their available equity without relinquishing interest rates below today’s prevailing rate on their first-lien mortgages. However, with the recently passed tax reform package, interest on these lines of credit will no longer be deductible, which increases the post-tax expense of HELOCs for those who itemize. While there are obviously multiple factors to consider when identifying which method of equity extraction makes more financial sense for a given borrower, in many cases, for those with high unpaid principal balances who are taking out lower line amounts, the math still favors HELOCs. However – assuming interest on cash-out refinances remains deductible – for low-to-moderate UPB borrowers taking out larger amounts of equity, the post-tax math for those who will still itemize under the increased standard deduction may now favor cash-out refinances instead, even if the result is a slight increase to first-lien interest rates.
“As rates continue to rise and the cost associated with increasing the rate on an entire first-lien balance rises as well, the benefit pendulum will likely swing back toward HELOCs. Even so, the change could certainly impact HELOC lending volumes and loan amounts in the coming months and years. To a certain degree, the same question holds true for cash-out refinances, since tax debt for homeowners who will no longer itemize becomes generally more expensive without mortgage interest deduction in the equation. These refinances will likely be an attractive source of secured debt in the future, but increased post-tax costs may have a negative impact on originations. That said, it still remains to be seen whether and to what extent tax costs will impact borrower decisions in terms of either HELOCs or cash-out refinances. At this point, only time will tell.”
The increase in equity, driven by rising home prices, has also continued to shrink the population of underwater borrowers who owe more on their mortgages than their homes are worth. The number of underwater borrowers declined by 800,000 over the first nine months of 2017, a 37 percent decline in negative equity since the start of the year. Only 2.7 percent of homeowners with a mortgage (approximately 1.36 million borrowers) now owe more than their home is worth, the lowest such rate since 2006. Though still elevated from pre-recession levels, the negative equity rate continues to normalize. Even so, home prices in large portions of the country remain below pre-recession peaks. While 36 states and 70 percent of Core Based Statistical Areas (CBSAs) have now surpassed pre-recession home price peaks, 43 of the nation’s 100 largest markets still lag behind.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graphic from Black Knight shows the number of homeowners with negative equity over time.
From Black Knight:
• The number of underwater borrowers declined by 800K over the first nine months of 2017, a 37 percent decline since the start of the yearThere is much more in the mortgage monitor.
• Only 2.7 percent of homeowners with a mortgage (1.36M) now owe more on their mortgages than their homes are worth, the lowest such rate since 2006
• Though the national negative equity rate remains elevated from pre-recession levels, it is certainly normalizing


