by Calculated Risk on 3/23/2022 07:00:00 AM
Wednesday, March 23, 2022
MBA: Mortgage Applications Decrease in Latest Weekly Survey
From the MBA: Mortgage Applications Decrease in Latest MBA Weekly Survey
Mortgage applications decreased 8.1 percent from one week earlier, according to data from the Mortgage Bankers Association’s (MBA) Weekly Mortgage Applications Survey for the week ending March 18, 2022.
... The Refinance Index decreased 14 percent from the previous week and was 54 percent lower than the same week one year ago. The seasonally adjusted Purchase Index decreased 2 percent from one week earlier. The unadjusted Purchase Index decreased 1 percent compared with the previous week and was 12 percent lower than the same week one year ago.
“Rates on 30-year conforming mortgages jumped by 23 basis points last week, the largest weekly increase since March 2020. The jump in rates comes as markets moved to price in a much faster pace of rate hikes, as well as expectations of fewer MBS purchases from the Federal Reserve. With mortgage rates now at 4.5 percent, compared to rates at or below 3 percent not that long ago, it is no surprise that refinance volume has dropped by more than 50 percent compared to this time last year. MBA’s new March forecast expects mortgage rates to continue to trend higher through the course of 2022,” said Mike Fratantoni, MBA’s Senior Vice President and Chief Economist. “Purchase application volume was down slightly for the week, with a larger drop in FHA and VA purchase volume, and a small decline in conventional purchase loans. First-time homebuyers, who rely on these government programs, are increasingly challenged by both the rapid increase in home prices and higher mortgage rates. Repeat homebuyers, who are more likely to use conventional loans, benefit from the gains in home equity realized on a sale which can be used to fuel their next purchase, even with rates moving higher.”
...
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages with conforming loan balances ($647,200 or less) increased to 4.50 percent from 4.27 percent, with points increasing to 0.59 from 0.54 (including the origination fee) for 80 percent loan-to-value ratio (LTV) loans.
emphasis added
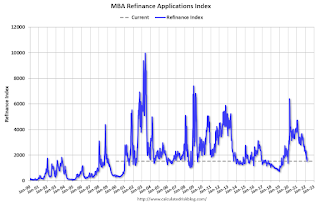 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph shows the refinance index since 1990.
The second graph shows the MBA mortgage purchase index
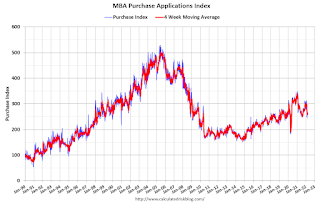 According to the MBA, purchase activity is down 12% year-over-year unadjusted.
According to the MBA, purchase activity is down 12% year-over-year unadjusted.Note: Red is a four-week average (blue is weekly).
Tuesday, March 22, 2022
Wednesday: New Home Sales
by Calculated Risk on 3/22/2022 09:27:00 PM
Wednesday:
• At 7:00 AM ET, The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) will release the results for the mortgage purchase applications index.
• At 8:00 AM, Discussion, Fed Chair Powell, Panel on Emerging Challenges for Central Bank Governors in a Digital World, At the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Innovation Summit 2022 (Virtual)
• At 10:00 AM, New Home Sales for February from the Census Bureau. The consensus is for 815 thousand SAAR, up from 801 thousand in January.
• During the day, The AIA's Architecture Billings Index for February (a leading indicator for commercial real estate).
On COVID (focus on hospitalizations and deaths):
| COVID Metrics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Now | Week Ago | Goal | ||
| Percent fully Vaccinated | 65.4% | --- | ≥70.0%1 | |
| Fully Vaccinated (millions) | 217.1 | --- | ≥2321 | |
| New Cases per Day3 | 28,657 | 31,558 | ≤5,0002 | |
| Hospitalized3 | 18,203 | 25,105 | ≤3,0002 | |
| Deaths per Day3 | 861 | 1,167 | ≤502 | |
| 1 Minimum to achieve "herd immunity" (estimated between 70% and 85%). 2my goals to stop daily posts, 37-day average for Cases, Currently Hospitalized, and Deaths 🚩 Increasing 7-day average week-over-week for Cases, Hospitalized, and Deaths ✅ Goal met. | ||||
This graph shows the daily (columns) and 7-day average (line) of deaths reported.
March Vehicle Sales Forecast: Decrease to 13.4 million SAAR
by Calculated Risk on 3/22/2022 05:51:00 PM
From WardsAuto: Forecast March U.S. Light-Vehicle Sales: SAAR Down from February but First-Quarter Results Best Since Q2-2021 (pay content)
Supply issues continue to impact vehicle sales, but it appears the supply chain disruption bottom is in.

This graph shows actual sales from the BEA (Blue), and Wards forecast for March (Red).
The Wards forecast of 13.4 million SAAR, would be down about 5% from last month, and down 24% from a year ago (sales were solid in March 2021, as sales recovered from the depths of the pandemic, and weren't yet impacted by supply chain issues).
Distressing Gap: Existing and New Home Sales
by Calculated Risk on 3/22/2022 02:30:00 PM
By request, here is an update to the "distressing gap" graph that I first started posting following the housing bubble to show the emerging gap caused by distressed sales.
I haven't posted this in a couple of years since the pandemic distorted the numbers.
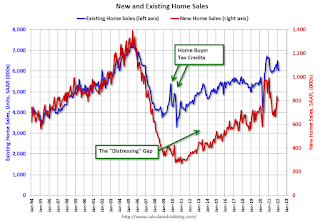
Following the housing bubble and bust, the "distressing gap" appeared mostly because of distressed sales.
In 2020, the gap was mostly closed with help from the pandemic.
 Another way to look at this is a ratio of existing to new home sales.
Another way to look at this is a ratio of existing to new home sales.This ratio was fairly stable from 1994 through 2006, and then the flood of distressed sales kept the number of existing home sales elevated and depressed new home sales. (Note: This ratio was fairly stable back to the early '70s, but I only have annual data for the earlier years).
In general, the ratio has been trending down since the housing bust - and was close to the historical ratio before the pandemic.
Note: Existing home sales are counted when transactions are closed, and new home sales are counted when contracts are signed. So, the timing of sales is different.
Mortgage Rates Moving Closer to 5%
by Calculated Risk on 3/22/2022 11:21:00 AM
Today, in the Calculated Risk Real Estate Newsletter: Mortgage Rates Moving Closer to 5%
A brief excerpt:
Mortgage News Daily reports that the most prevalent 30-year fixed rate is now at 4.66% for top tier scenarios. Matthew Graham at Mortgage News Daily wrote yesterday: Bond Market Betrayal as Mortgage Rates Hit Another Long Term HighThere is much more in the article. You can subscribe at https://calculatedrisk.substack.com/The event in question was a speech (and subsequent comments) from Fed Chair Powell. Rather than do anything at all to push back against last week's Fed-driven rate spike, Powell forcefully doubled down on the Fed's urgent need to shift Fed policy to an even less rate-friendly stance.
Mortgage lenders were already roughly an eighth of a point higher in terms of 30yr fixed rates this morning. After Powell, rates nearly doubled that move (i.e. some lenders are a quarter of a point higher in rate versus Friday's latest levels). That makes today one of only 5 days with this big of a spike in more than a decade.
Lender rate offerings are widely stratified and many are still getting caught up with the market volatility, but it's safe to say the average lender is now over 4.5%, and much closer to 4.625% for top tier conventional 30yr fixed scenarios.Of course, rates are still historically low. But rates are up sharply from the recent lows, and my view is the change in rates is what will impact housing (see my post last week: Housing, the Fed, Interest Rates and Inflation; Housing is a key transmission mechanism for the FOMC). Here is a long-term graph of 30-year mortgage rates (Freddie Mac PMMS, February is today’s rate).
Goldman: Expecting Fed to hike 50bps in May and Start Balance Sheet Reduction
by Calculated Risk on 3/22/2022 09:29:00 AM
A few excerpt from a Goldman Sachs research note: Moving “Expeditiously” Implies a Faster Pace; Forecasting 50bp Hikes in May and June
In a speech [yesterday], Chair Powell said, “There is an obvious need to move expeditiously to return the stance of monetary policy to a more neutral level, and then to move to more restrictive levels if that is what is required to restore price stability.” He repeated the call “to move expeditiously” at the end of the speech. ... We now forecast 50bp hikes at both the May and June meetings, followed by 25bp hikes at the four remaining meetings in the back half of 2022 ... We continue to expect the FOMC to announce the start of balance sheet reduction at the May meeting.CNBC's Steve Liesman tweeted this morning:
emphasis added
"The Dec. Fed Funds contract trades with an implied yield of 2.13... that means 7 MORE hikes from here or 8 total this year. At least one of those meetings needs to be 50bp. The 50bp probability for May is 68%. There is also going to be balance sheet reduction."So a 50bps hike - and balance sheet reduction - are becoming the consensus view.
Monday, March 21, 2022
Tuesday: Richmond Fed Mfg
by Calculated Risk on 3/21/2022 09:00:00 PM
From Matthew Graham at Mortgage News Daily: From Bad to Worse as Powell Doubles Down on Policy Shift
Things were already fairly ugly this morning as the bond market opted to pay no attention to last Friday's consolidation potential. Fed Funds Futures showed the market pricing in at least one 50bp hike in addition to a 25bp hike at every remaining Fed meeting this year. Powell's scheduled speech added a significant amount of fuel to that fire at 12:30pm. He did nothing to try to calm the market down, but instead, essentially told traders they were correct in rushing to price in more rate hikes and faster policy normalization. This resulted in overnight losses more than doubling across the curve, and widespread negative reprices. [30 year fixed 4.66%]Tuesday:
emphasis added
• At 10:00 AM ET, Richmond Fed Survey of Manufacturing Activity for March.
On COVID (focus on hospitalizations and deaths):
| COVID Metrics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Now | Week Ago | Goal | ||
| Percent fully Vaccinated | 65.4% | --- | ≥70.0%1 | |
| Fully Vaccinated (millions) | 217.1 | --- | ≥2321 | |
| New Cases per Day3 | 27,786 | 33,721 | ≤5,0002 | |
| Hospitalized3 | 18,203 | 25,105 | ≤3,0002 | |
| Deaths per Day3 | 901 | 1,187 | ≤502 | |
| 1 Minimum to achieve "herd immunity" (estimated between 70% and 85%). 2my goals to stop daily posts, 37-day average for Cases, Currently Hospitalized, and Deaths 🚩 Increasing 7-day average week-over-week for Cases, Hospitalized, and Deaths ✅ Goal met. | ||||
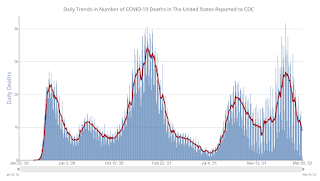 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the daily (columns) and 7-day average (line) of deaths reported.
MBA Survey: "Share of Mortgage Loans in Forbearance Decreases to 1.18% in February"
by Calculated Risk on 3/21/2022 04:00:00 PM
Note: This is as of February 28th.
From the MBA: Share of Mortgage Loans in Forbearance Decreases to 1.18% in February
The Mortgage Bankers Association’s (MBA) monthly Loan Monitoring Survey revealed that the total number of loans now in forbearance decreased by 12 basis points from 1.30% of servicers’ portfolio volume in the prior month to 1.18% as of February 28, 2022. According to MBA’s estimate, 590,000 homeowners are in forbearance plans.
The share of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac loans in forbearance decreased 8 basis points to 0.56%. Ginnie Mae loans in forbearance decreased 10 basis points to 1.50%, and the forbearance share for portfolio loans and private-label securities (PLS) declined 30 basis points to 2.72%
“There were many positive results in overall mortgage performance in February. The percentage of borrowers in forbearance declined for the 21st consecutive month, and the percentage of borrowers current on their mortgage payments increased to almost 95 percent – 350 basis points higher than one year ago. Finally, the percentage of borrowers with existing loan workouts who were current on their mortgage payments improved for the first time since June 2021,” said Marina Walsh, CMB, MBA’s Vice President of Industry Analysis. “These three results – the lower forbearance rates and higher performance rates for both total borrowers and borrowers in workouts – are especially favorable given that there is typically a dip in mortgage performance in February because of the shortened number of days to make a payment.”
Added Walsh, “We can credit several factors to the improved performance, including the availability of viable loss mitigation options, low unemployment that is now below 4.0 percent, strong wage growth, and rising home equity."
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the percent of portfolio in forbearance by investor type over time. The number of forbearance plans is decreasing.
Final Look at Local Housing Markets in February
by Calculated Risk on 3/21/2022 03:10:00 PM
Today, in the Calculated Risk Real Estate Newsletter: Final Look at Local Housing Markets in February
A brief excerpt:
This update adds Columbus, Illinois, Indiana, Maryland, Miami, New York, Pennsylvania, Phoenix, Rhode Island and Washington, D.C.There is much more in the article. You can subscribe at https://calculatedrisk.substack.com/
My view is that if the housing market starts slowing, it will show up in inventory first.
...
Here is a summary of active listings for these housing markets in February. Inventory was down 3.8% in February month-over-month (MoM) from January, and down 28.0% year-over-year (YoY).
It appears inventory has bottomed seasonally in some areas. Last month, these markets were down 30.5% YoY, so the YoY decline in February is smaller than in January. This isn’t indicating a slowing market, but maybe a few baby steps towards a more balanced market in some areas.
Notes for all tables:
1. New additions to table in BOLD.
2. Northwest (Seattle), North Texas (Dallas), and Santa Clara (San Jose), Jacksonville, Source: Northeast Florida Association of REALTORS®
3. Totals do not include Atlanta, Denver, Minneapolis (included in state totals).
Fed Chair Powell: FOMC "Not assuming significant near-term supply-side relief" on inflation
by Calculated Risk on 3/21/2022 12:34:00 PM
From Fed Chair Powell: Restoring Price Stability. Excerpt on inflation:
Turning to price stability, the inflation outlook had deteriorated significantly this year even before Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
The rise in inflation has been much greater and more persistent than forecasters generally expected. For example, at the time of our June 2021 meeting, every Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) participant and all but one of 35 submissions in the Survey of Professional Forecasters predicted that 2021 inflation would be below 4 percent. Inflation came in at 5.5 percent.
For a time, moderate inflation forecasts looked plausible—the one-month headline and core inflation rates declined steadily from April through September. But inflation moved up sharply in the fall, and, just since our December meeting, the median FOMC projection for year-end 2022 jumped from 2.6 percent to 4.3 percent.
Why have forecasts been so far off? In my view, an important part of the explanation is that forecasters widely underestimated the severity and persistence of supply-side frictions, which, when combined with strong demand, especially for durable goods, produced surprisingly high inflation.
The pandemic and the associated shutdown and reopening of the economy caused a serious upheaval in many parts of the economy, snarling supply chains, constraining labor supply, and creating a major boom in demand for goods and a bust in services demand. The combination of the surge in goods demand with supply chain bottlenecks led to sharply rising goods prices (figure 4). The most notable example here is motor vehicles. Prices soared across the vehicles sector as booming demand was met by a sharp decline in global production during the summer of 2021, owing to shortages of computer chips. Production remains below pre-pandemic levels, and an expected sharp decline in prices has been repeatedly postponed.
Many forecasters, including FOMC participants, had been expecting inflation to cool in the second half of last year, as the economy started going back to normal after vaccines became widely available.3 Expectations were that the supply-side damage would begin to heal. Schools would reopen—freeing parents to return to work—and labor supply would begin bouncing back, kinks in supply chains would begin resolving, and consumption would start rotating back to services, all of which could reduce price pressures. While schools are open, none of the other expectations has been fully met. Part of the reason may be that, contrary to expectations, COVID has not gone away with the arrival of vaccines. In fact, we are now headed once again into more COVID-related supply disruptions from China. It continues to seem likely that hoped-for supply-side healing will come over time as the world ultimately settles into some new normal, but the timing and scope of that relief are highly uncertain. In the meantime, as we set policy, we will be looking to actual progress on these issues and not assuming significant near-term supply-side relief.
emphasis added


