by Calculated Risk on 4/04/2023 01:00:00 PM
Tuesday, April 04, 2023
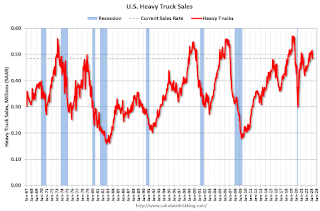
Heavy Truck Sales Up 7% Year-over-year in March
This graph shows heavy truck sales since 1967 using data from the BEA. The dashed line is the March 2023 seasonally adjusted annual sales rate (SAAR).
Heavy truck sales really collapsed during the great recession, falling to a low of 180 thousand SAAR in May 2009. Then heavy truck sales increased to a new all-time high of 570 thousand SAAR in April 2019.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Note: "Heavy trucks - trucks more than 14,000 pounds gross vehicle weight."
Heavy truck sales declined sharply at the beginning of the pandemic, falling to a low of 308 thousand SAAR in May 2020.
Moody's: Multifamily Demand "Softened notably over the past few quarters"
by Calculated Risk on 4/04/2023 11:15:00 AM
Today, in the Calculated Risk Real Estate Newsletter: Moody's: Multifamily Demand "Softened notably over the past few quarters"
A brief excerpt:
The big story here is that demand for apartments has softened recently, rents are falling in some areas, and there are a large number of apartments currently under construction that are expected to be delivered this year.There is more in the article. You can subscribe at https://calculatedrisk.substack.com/
From Moody’s Analytics Senior Economist Lu Chen and economist Nick Luettke: Apartment temporarily oversupplied, Office approaching peak of vacancy, and Retail remained flatThe tide has been gradually shifting for the multifamily sector. ... Multifamily demand has softened notably over the past few quarters with net absorption even teasing slightly below zero in the first quarter of 2023. ... Vacancy ticked up 13 basis-point (bps) to end Q1 at 4.71%. This was the biggest jump over the past two years, which pushed the current vacancy over the pre-pandemic level of 4.68%....
Compared to year end 2022, rent declines became more widespread in the first quarter, with 60 primary metros recording negative market rent growth ranging from -0.1% to -6.4%.Moody’s Analytics (Reis) reported that the apartment vacancy rate was at 4.7% in Q1 2023, up from 4.6% in Q4 2022, and down from a pandemic peak of 5.4% in both Q1 and Q2 2021.
This graph shows the apartment vacancy rate starting in 1980. (Annual rate before 1999, quarterly starting in 1999). Note: Moody’s Analytics is just for large cities.
BLS: Job Openings Decreased to 9.9 million in February
by Calculated Risk on 4/04/2023 10:07:00 AM
From the BLS: Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary
The number of job openings decreased to 9.9 million on the last business day of February, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Over the month, the number of hires and total separations changed little at 6.2 million and 5.8 million, respectively. Within separations, quits (4.0 million) edged up, while layoffs and discharges (1.5 million) decreased.The following graph shows job openings (black line), hires (dark blue), Layoff, Discharges and other (red column), and Quits (light blue column) from the JOLTS.
emphasis added
This series started in December 2000.
Note: The difference between JOLTS hires and separations is similar to the CES (payroll survey) net jobs headline numbers. This report is for February the employment report this Friday will be for March.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Note that hires (dark blue) and total separations (red and light blue columns stacked) are usually pretty close each month. This is a measure of labor market turnover. When the blue line is above the two stacked columns, the economy is adding net jobs - when it is below the columns, the economy is losing jobs.
The spike in layoffs and discharges in March 2020 is labeled, but off the chart to better show the usual data.
Jobs openings decreased in February to 9.9 million from 10.6 million in January.
The number of job openings (black) were down 14% year-over-year.
Quits were down 7% year-over-year. These are voluntary separations. (See light blue columns at bottom of graph for trend for "quits").
CoreLogic: House Prices up 4.4% YoY in February; Increased 0.8% MoM in February NSA
by Calculated Risk on 4/04/2023 08:00:00 AM
Notes: This CoreLogic House Price Index report is for February. The recent Case-Shiller index release was for January. The CoreLogic HPI is a three-month weighted average and is not seasonally adjusted (NSA).
From CoreLogic: US Annual Home Price Growth Continues Single-Digit Slide in February, CoreLogic Reports
CoreLogic® ... today released the CoreLogic Home Price Index (HPI™) and HPI Forecast™ for February 2023.
While annual U.S home price growth rose for the 133rd straight month in February, the 4.4% increase was the lowest recorded since 2019. Eight states and districts recorded annual home price losses, with much of the depreciation seen in the relatively expensive Western U.S., including California, Idaho, Oregon, Washington and Utah.
Tech company layoffs have likely affected housing demand on the West Coast, However, as noted in the latest CoreLogic S&P Case-Shiller Index, home prices gains are holding steady in some large East Coast metros, as workers return to offices and buyer demand renews in areas that saw relatively less appreciation during the pandemic. Areas in the Southern U.S. are also holding up well given current market conditions.
“The divergence in home price changes across the U.S. reflects a tale of two housing markets,” said Selma Hepp, chief economist at CoreLogic. “Declines in the West are due to the tech industry slowdown and a severe lack of affordability after decades of undersupply. The consistent gains in the Southeast and South reflect strong job markets, in-migration patterns and relative affordability due to new home construction.”
“But while housing market challenges remain, particularly in light of mortgage rate volatility and the ongoing banking turmoil,” Hepp continued, “pent-up homebuyer demand is responding favorably to lower rates in many markets. This trend holds true even in the West, leading to a solid monthly gain in home prices in February. U.S. home prices rose by 0.8% in February, double the month-over-month increase historically seen and indicating that prices in most markets have already bottomed out.”
...
U.S. home prices (including distressed sales) increased by 4.4% year over year in February 2023 compared to February 2022. On a month-over-month basis, home prices increased by 0.8% compared with January 2023.
emphasis added
Monday, April 03, 2023
Tuesday: Job Openings
by Calculated Risk on 4/03/2023 09:23:00 PM

Mortgage rates moved lower today as investors reacted to economic data that showed contraction in the manufacturing sector. ... After the data was released, the bond market swung from negative to positive territory. ...Tuesday:
With that, the average mortgage lender was able to drop rates to levels just a hair higher than the lows from March 23-24. You'd have to go back to February 3rd to see anything lower. With today being April 3rd, that means we're right on the doorstep of 2 month lows. [30 year fixed 6.44%]
emphasis added
• At 8:00 AM ET, Corelogic House Price index for February.
• At 10:00 AM, Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey for February from the BLS.
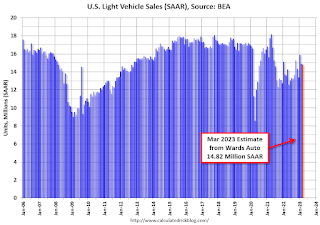
Vehicles Sales at 14.82 million SAAR in March; Up 9.3% YoY
by Calculated Risk on 4/03/2023 06:37:00 PM
Wards Auto released their estimate of light vehicle sales for March: Greater Availability, Rising Incentives Lead March U.S. Light-Vehicle Sales to 9% Gain (pay site).
Wards Auto estimates sales of 14.82 million SAAR in March 2023 (Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate), essentially unchanged from the February sales rate, and up 9.3% from March 2022.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows light vehicle sales since 2006 from the BEA (blue) and Wards Auto's estimate for March (red).
The impact of COVID-19 was significant, and April 2020 was the worst month. After April 2020, sales increased, and were close to sales in 2019 (the year before the pandemic). However, sales decreased in 2021 due to supply issues. It appears the "supply chain bottom" was in September 2021.
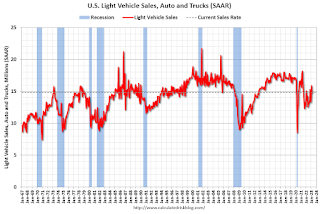 The second graph shows light vehicle sales since the BEA started keeping data in 1967.
The second graph shows light vehicle sales since the BEA started keeping data in 1967. Q1 2023 Update: Unofficial Problem Bank list Decreased to 46 Institutions
by Calculated Risk on 4/03/2023 04:21:00 PM
The FDIC's official problem bank list is comprised of banks with a CAMELS rating of 4 or 5, and the list is not made public (just the number of banks and assets every quarter). Note: Bank CAMELS ratings are also not made public.
CAMELS is the FDIC rating system, and stands for Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity and Sensitivity to market risk. The scale is from 1 to 5, with 1 being the strongest.
As a substitute for the CAMELS ratings, surferdude808 is using publicly announced formal enforcement actions, and also media reports and company announcements that suggest to us an enforcement action is likely, to compile a list of possible problem banks in the public interest.
DISCLAIMER: This is an unofficial list, the information is from public sources only, and while deemed to be reliable is not guaranteed. No warranty or representation, expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy of the information contained herein and same is subject to errors and omissions. This is not intended as investment advice. Please contact CR with any errors.
Here are the quarterly changes and a few comments from surferdude808:
Update on the Unofficial Problem Bank List through March 31, 2023. Since the last update at the end of December 2022, the list decreased by three to 46 institutions after three removals. Assets decreased by $1.7 billion to $49.3 billion, about one-third of the drop was because of a $787 million decline from updated asset figures through December 31, 2022. A year ago, the list held 54 institutions with assets of $60.9 billion. Removals during the quarter because of action termination included Carver Federal Savings Bank, New York, NY ($713 million) and The City National Bank of Colorado City, Colorado City, TX ($237 million). First Savanna Savings Bank, Savanna, IL ($9 million) found its way off this list through a voluntary merger.
With the conclusion of the fourth quarter, we bring an updated transition matrix to detail how banks are transitioning off the Unofficial Problem Bank List. Since we first published the Unofficial Problem Bank List on August 7, 2009 with 389 institutions, 1,789 institutions have appeared on a weekly or monthly list since then. Only 2.6 percent of the banks that have appeared on a list remain today as 1,743 institutions have transitioned through the list. Departure methods include 1,031 action terminations, 411 failures, 282 mergers, and 19 voluntary liquidations. Of the 389 institutions on the first published list, only 3 or less than 1.0 percent, still have a troubled designation more than ten years later. The 411 failures represent 23 percent of the 1,789 institutions that have made an appearance on the list. This failure rate is well above the 10-12 percent rate frequently cited in media reports on the failure rate of banks on the FDIC's official list.
On February 28, 2023, the FDIC released fourth quarter results and provided an update on the Official Problem Bank List. While FDIC did not make a comment within its press release on the Official Problem Bank List, they provided details in an attachment that listed 39 institutions with assets of $47 billion. These figures were notable lower from last quarter when the FDIC said the Official Problem List had 42 institutions with assets of $164 billion. Hence during the quarter, the large unknown depository was removed. The $116 billion decline in assets provides some clues as to that unknown depository. At December 31, 2022, there were three depositories -- UBS Bank USA ($121 billion); USAA Federal Savings Bank ($111 billion); and First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company ($109 billion). Since First-Citizens Bank & Trust Company, it was likely not them as they are a SEC registrant and an enforcement action would be considered a material event requiring disclosure. Given that the parent of UBS Bank just acquired Credit Suisse, would they have been approved to complete that acquisition with a troubled subsidiary? Emergencies do cause the authorities to approve transactions that would not be permitted in stable periods. USAA Federal Savings Bank appears to be owned by its policyholders; if so, then it would not be subject to SEC disclosure rules. A few names, some details on their circumstances, we will let you handicap who the unknown whale was.
Since we last checked in with, there has been another banking sector dislocation event. There have been three bank failures – Silvergate Bank, Silicon valley Bank, and Signature Bank. Some common risk characteristics of the failed banks include a deposit base that was mostly uninsured (“hot money’), lack of diversification (industry, business line, and customer concentrations), and poorly managed liquidity position (illiquid securities that could not be sold). The large volume of uninsured deposits triggered runs at other depositories, forcing a systemic risk declaration to protect the uninsured depositors at Signature Bank and Silicon Valley Bank. Hearings this past week on the Hill exposed failures in the supervisory process and regulatory framework. Informed readers here know that before a bank fails, the risks should be identified by regulators and a corrective program be in place. In short, the bank should be operating under a formal enforcement action before it goes belly up. That was not the case here, as all three banks went straight to failure bypassing the desired orderly resolution. These failures messy and very disorderly. Hopefully, some prudent reforms are put in place to prevent a re-occurrence.
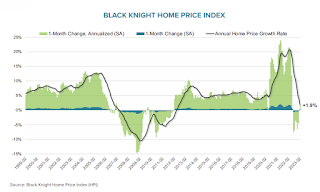
Black Knight Mortgage Monitor: Home Prices Increased Slightly in February; Prices Up 1.9% YoY
by Calculated Risk on 4/03/2023 11:14:00 AM
Today, in the Calculated Risk Real Estate Newsletter: Black Knight Mortgage Monitor: Home Prices Increased Slightly in February; Prices Up 1.9% YoY
A brief excerpt:
Here is a graph of the Black Knight HPI. The index is still up 1.9% year-over-year and will likely turn negative YoY soon.There is much more in the article. You can subscribe at https://calculatedrisk.substack.com/
• A modest easing of affordability in January and early February along with tightening inventory levels drove home prices slightly higher
• On an adjusted basis, prices were up 0.16% for the month, the strongest single month gain since May of last year, while non-adjusted they were up 0.68%
• The headline annual home price growth rate fell by 164 bps in the month to 1.94%, the first time we’ve seen annual home price growth below 2% since early 2012
• Price growth is expected to cross over into negative territory by April but may return above 0% before the end of the year if inventory challenges persist and interest rates ease
• All in, home prices nationally are now down 2.6% from their 2022 peak, marginally improved from 2.7% in January
emphasis added
Construction Spending Decreased 0.1% in February
by Calculated Risk on 4/03/2023 10:21:00 AM
From the Census Bureau reported that overall construction spending decreased:
Construction spending during February 2023 was estimated at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $1,844.1 billion, 0.1 percent below the revised January estimate of $1,845.4 billion. The February figure is 5.2 percent above the February 2022 estimate of $1,753.1 billion.Private spending was "virtually unchanged" and public spending decreased:
emphasis added
Spending on private construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $1,453.2 billion, virtually unchanged from the revised January estimate of $1,453.6 billion. ...
In February, the estimated seasonally adjusted annual rate of public construction spending was $391.0 billion, 0.2 percent below the revised January estimate of $391.8 billion.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows private residential and nonresidential construction spending, and public spending, since 1993. Note: nominal dollars, not inflation adjusted.
Residential (red) spending is 9.8% below the recent peak.
Non-residential (blue) spending is at a new peak.
Public construction spending is close to the recent peak.
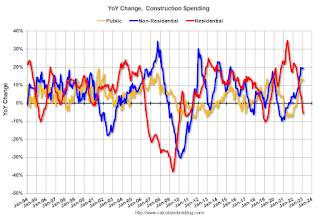 The second graph shows the year-over-year change in construction spending.
The second graph shows the year-over-year change in construction spending.On a year-over-year basis, private residential construction spending is down 5.7%. Non-residential spending is up 19.4% year-over-year. Public spending is up 12.8% year-over-year.
ISM® Manufacturing index Decreased to 46.3% in March
by Calculated Risk on 4/03/2023 10:04:00 AM
(Posted with permission). The ISM manufacturing index indicated contraction. The PMI® was at 46.3% in March, down from 47.7% in February. The employment index was at 46.9%, down from 49.1% last month, and the new orders index was at 44.3%, up from 47.0%.
From ISM: Manufacturing PMI® at 46.3%
March 2023 Manufacturing ISM® Report On Business®
Economic activity in the manufacturing sector contracted in March for the fifth consecutive month following a 28-month period of growth, say the nation's supply executives in the latest Manufacturing ISM® Report On Business®.This suggests manufacturing contracted in March. This was below the consensus forecast.
The report was issued today by Timothy R. Fiore, CPSM, C.P.M., Chair of the Institute for Supply Management® (ISM®) Manufacturing Business Survey Committee:
“The March Manufacturing PMI® registered 46.3 percent, 1.4 percentage points lower than the 47.7 percent recorded in February. Regarding the overall economy, this figure indicates a fourth month of contraction after a 30-month period of expansion. The Manufacturing PMI® is at its lowest level since May 2020, when it registered 43.5 percent. The New Orders Index remained in contraction territory at 44.3 percent, 2.7 percentage points lower than the figure of 47 percent recorded in February. The Production Index reading of 47.8 percent is a 0.5-percentage point increase compared to February’s figure of 47.3 percent. The Prices Index registered 49.2 percent, down 2.1 percentage points compared to the February figure of 51.3 percent. The Backlog of Orders Index registered 43.9 percent, 1.2 percentage points lower than the February reading of 45.1 percent. The Employment Index continued in contraction territory, registering 46.9 percent, down 2.2 percentage points from February’s reading of 49.1 percent. The Supplier Deliveries Index figure of 44.8 percent is 0.4 percentage point lower than the 45.2 percent recorded in February; this is the index’s lowest reading since March 2009 (43.2 percent). The Inventories Index dropped into contraction at 47.5 percent, 2.6 percentage points lower than the February reading of 50.1 percent. The New Export Orders Index reading of 47.6 percent is 2.3 percentage points lower than February’s figure of 49.9 percent. The Imports Index continued in contraction territory at 47.9 percent, 2 percentage points below the 49.9 percent reported in February.”
emphasis added