by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 06:36:00 PM
Thursday, September 10, 2009
Fed Vice Chairman Kohn on Monetary Policy
This speech is a review of an academic paper (and a bit wonkish) ... here are some excerpts on two key topics: 1) how well the Fed followed the precepts of Walter Bagehot, and 2) if the Fed should target a higher inflation rate in a liquidity trap.
From Federal Reserve Vice Chairman Donald Kohn: Comments on "Interpreting the Unconventional U.S. Monetary Policy of 2007-2009"
... In designing our liquidity facilities we were guided by the time-tested precepts derived from the work of Walter Bagehot. Those precepts hold that central banks can and should ameliorate financial crises by providing ample credit to a wide set of borrowers, as long as the borrowers are solvent, the loans are provided against good collateral, and a penalty rate is charged.Clearly the Fed believes - except in a few special circumstances - that they did not take on significant credit risk.
..
The liquidity measures we took during the financial crisis, although unprecedented in their details, were generally consistent with Bagehot's principles and aimed at short-circuiting these feedback loops. The Federal Reserve lends only against collateral that meets specific quality requirements, and it applies haircuts where appropriate. Beyond the collateral, in many cases we also have recourse to the borrowing institution for repayment. In the case of the TALF, we are backstopped by the Treasury. In addition, the terms and conditions of most of our facilities are designed to be unattractive under normal market conditions, thus preserving borrowers' incentives to obtain funds in the market when markets are operating normally. Apart from a very small number of exceptions involving systemically important institutions, such features have limited the extent to which the Federal Reserve has taken on credit risk, and the overall credit risk involved in our lending during the crisis has been small.
In Ricardo's view, if the collateral had really been good, private institutions would have lent against it. However, as has been recognized since Bagehot, private lenders, acting to protect themselves, typically severely curtail lending during a financial crisis, irrespective of the quality of the available collateral. The central bank--because it is not liquidity constrained and has the infrastructure in place to make loans against a variety of collateral--is well positioned to make those loans in the interest of financial stability, and can make them without taking on significant credit risk, as long as its lending is secured by sound collateral. A key function of the central bank is to lend in such circumstances to contain the crisis and mitigate its effects on the economy.
emphasis added
And on monetary policy in a liquidity trap:
Ricardo notes that the theoretical literature on monetary policy in a liquidity trap commonly prescribes targeting higher-than-normal inflation rates even beyond the point of economic recovery, so that real interest rates decline by more and thus provide greater stimulus for the economy. The arguments in favor of such a policy hinge on a clear understanding on the part of the public that the central bank will tolerate increased inflation only temporarily--say, for a few years once the economy has recovered--before returning to the original inflation target in the long term. Notably, although many central banks have put their policy rates near zero, none have adopted this prescription. In the theoretical environment considered by the paper, long-run inflation expectations are perfectly anchored. In reality, however, the anchoring of inflation expectations has been a hard-won achievement of monetary policy over the past few decades, and we should not take this stability for granted. Models are by their nature only a stylized representation of reality, and a policy of achieving "temporarily" higher inflation over the medium term would run the risk of altering inflation expectations beyond the horizon that is desirable. Were that to happen, the costs of bringing expectations back to their current anchored state might be quite high. But while the Federal Reserve has not attempted to raise medium-term inflation expectations as prescribed by the theories discussed in the paper, it has taken numerous steps to lower real interest rates for private borrowers and keep inflation expectations from slipping to undesirably low levels in order to prevent unwanted disinflation. These steps include the credit policies I discussed earlier, the provision of forward guidance that the level of short-term interest rates is expected to remain quite low "for an extended period" conditional on the outlook for the economy and inflation, and the publication of the longer-run inflation objectives of FOMC members.There are both interesting topics. If the collateral is mostly solid (or the haircuts appropriate), then the Fed will be in decent shape when they start to unwind current policy positions. However Reis (no link) apparently argues that the Fed will suffer significant losses, and the borrowing from the Treasury will make the Fed's monetary policy less independent.
MEW and the Wealth Effect
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 02:50:00 PM
Professors Atif Mian and Amir Sufi (both University of Chicago Booth School of Business and NBER) published a new paper: The Household Leverage-Driven Recession of 2007 to 2009 This is related to their paper earlier this year: House Prices, Home Equity-Based Borrowing, and the U.S. Household Leverage Crisis, See: MEW, Consumption and Personal Saving Rate
A cross-sectional analysis of U.S. counties shows that areas with modest increases in leverage from 2002 to 2006 have experienced only a minor economic downturn, whereas counties with large increases in household leverage from 2002 to 2006 have experienced a severe recession. Our findings suggest that the process of household de-leveraging is likely to be the major headwind facing the economy going forward.The authors have written a brief discussion of the paper at NPR Money: Lessons From The Fall: Household Debt Got Us Into This Mess
The Economist has a recent review of the paper: Withdrawal symptoms
More than a third of new defaults in 2006-08 were because of home-equity-based borrowing. Default rates for low credit-quality homeowners rose by more than 12 percentage points in places where housing was scarcest and prices had risen most. In “elastic” cities, by contrast, the increase was less than four percentage points. This suggests huge over-borrowing. Prospects for a sustained recovery look dim if households that are most inclined to spend are mired in negative equity.Here are three graphs from the paper (posted with permission from the author):
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph is figure 5B from the paper. Looking at the left panel, note that the x-axis is the change in debt to income, by County, from 2002 to 2006. And the y-axis is for the period 2006 - 2008. This shows that the change in the debt to income ratio was a good predictor of default rates.
From the authors:
Correlation across Counties of Default Rates and House Prices during Recession with Leverage Growth from 2002 t0 2006
The left panel presents the correlation across U.S. counties of the increase in the household debt to income ratio from 2002 to 2006 and the increase in the default rate from 2006 to 2008. The right panel presents the correlation across U.S. counties of the increase in the household debt to income ratio from 2002 to 2006 and the decline in house prices from 2006 to 2008. The sample includes 450 counties with at least 50,000 households as of 2000.
 The second graph is figure 6A from the paper. From the authors:
The second graph is figure 6A from the paper. From the authors: Auto Sales and Unemployment Rates in High and Low Leverage Growth Counties
High leverage growth counties are defined to be the top 10% of counties by the increase in the debt to income ratio from 2002 to 2006. Low leverage growth counties are in the bottom 10% on the same measure. The left panel plots the growth in auto sales for high and low leverage growth counties since 2005, and the right panel plots the change in the unemployment rate in high and low leverage growth counties since 2005. Auto sales decline and unemployment increases by significantly more in counties that experience the sharpest increase in debt to income ratios from 2002 to 2006.
 The third graph is figure 6B from the paper. From the authors:
The third graph is figure 6B from the paper. From the authors: Correlation across Counties of Auto Sales and Unemployment during Recession with Leverage Growth from 2002 to 2006This analysis, comparing high and low leverage counties, is very revealing and shows that the high leverage areas are also the hardest hit (not surprising to those of us who felt mortgage equity extraction was a significant driver of consumption growth). The authors conclude:
The left panel presents the correlation across U.S. counties of the increase in the household debt to income ratio from 2002 to 2006 and the decline in auto sales from 2006 to 2008. The right panel presents the correlation across U.S. counties of the increase in the household debt to income ratio from 2002 to 2006 and the increase in unemployment rates from 2006 to 2008. The sample includes 450 counties with at least 50,000 households as of 2000.
[T]he initial economic slowdown was a direct result of an over-leveraged household sector unable to keep pace with its debt obligations.
Census Bureau: Real Median Household Income Fell 3.6%
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 11:39:00 AM
From the Census Bureau:
The U.S. Census Bureau announced today that real median household income in the United States fell 3.6 percent between 2007 and 2008, from$52,163 to $50,303. This breaks a string of three years of annual income increases and coincides with the recession that started in December 2007.Here are some interesting stats on income: Annual Social and Economic (ASEC) Supplement
The nation’s official poverty rate in 2008 was 13.2 percent, up from 12.5 percent in 2007. There were 39.8 million people in poverty in 2008, up from 37.3 million in 2007.
Meanwhile, the number of people without health insurance coverage rose from 45.7 million in 2007 to 46.3 million in 2008, while the percentage remained unchanged at15.4 percent.
...
•Income inequality was statistically unchanged between 2007 and 2008, as measured by shares of aggregate household income by quintiles and the Gini index. The Gini index was 0.466 in 2008.
Note: for the house price to household income chart I graph every quarter, I assumed a "2% increase in household [nominal] median income for 2008 and flat for 2009". That was too optimistic.
Report: Treasury to Announce Short Sale Incentives this Month
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 11:02:00 AM
From Diana Golobay at Housing Wire: Federal Incentives Coming for Short Sales, Deeds-in-Lieu
US Treasury Department sources confirmed to HousingWire the Treasury expects to issue details on the short sale and deed-in-lieu program later this month.This program is aimed at borrowers who would be "generally eligible for a MHA modification", but are probably too far underwater ... or owe too much.
...
[Federal Housing Administration (FHA) commissioner David Stevens said, in prepared remarks, at a House Financial Services subcommittee hearing yesterday:] “Because we know that the MHA program will not reach every at-risk homeowner or prevent all foreclosures, on May 14th the Administration announced the Foreclosure Alternatives program that will provide incentives for, and encourage, servicers and borrowers to pursue short sales and deeds-in-lieu (DIL) of foreclosure in cases where the borrower is generally eligible for a MHA modification but does not qualify or is unable to complete the process.”
He said the program will simplify the process of pursuing short sales and deeds-in-lieu, which will encourage more servicers and borrowers to participate in the program. The program will standardize the process, documentation and short performance timeframes.
“These options eliminate the need for potentially lengthy and expensive foreclosure proceedings, preserve the physical condition and value of the property by reducing the time a property is vacant, and allows the homeowners to transition with dignity to more affordable housing,” Stevens added.
emphasis added
Trade Deficit Increases in July
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 08:46:00 AM
The Census Bureau reports:
The ... total July exports of $127.6 billion and imports of $159.6 billion resulted in a goods and services deficit of $32.0 billion, up from $27.5 billion in June, revised.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph shows the monthly U.S. exports and imports in dollars through July 2009.
Imports were up again in July, and exports also increased. On a year-over-year basis, exports are off 22% and imports are off 30%.
The second graph shows the U.S. trade deficit, with and without petroleum, through July.
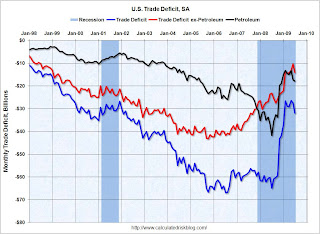 The blue line is the total deficit, and the black line is the petroleum deficit, and the red line is the trade deficit ex-petroleum products.
The blue line is the total deficit, and the black line is the petroleum deficit, and the red line is the trade deficit ex-petroleum products.Import oil prices increased to $62.48 in July - up about 50% from the prices in February (at $39.22) - and the fifth monthly increase in a row. Import oil prices will probably rise further in August.
It appears the cliff diving for U.S. trade might be over, although recent port data shows some weakness in traffic.
Weekly Unemployment Claims Decline
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 08:31:00 AM
The DOL reports weekly unemployment insurance claims decreased to 550,000:
In the week ending Sept. 5, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 550,000, a decrease of 26,000 from the previous week's revised figure of 576,000. The 4-week moving average was 570,000, a decrease of 2,750 from the previous week's revised average of 572,750.
...
The advance number for seasonally adjusted insured unemployment during the week ending Aug. 29 was 6,088,000, a decrease of 159,000 from the preceding week's revised level of 6,247,000.
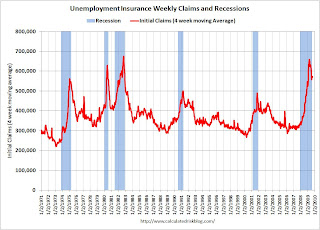 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.This graph shows the 4-week moving average of weekly claims since 1971.
The four-week average of weekly unemployment claims decreased this week by 1,250 to 570,000, and is now 88,750 below the peak in April.
It appears that initial weekly claims have peaked for this cycle. However it seem that weekly claims are stuck at a very high level; weekly claims have been in the high 500 thousands for 10 weeks. This indicates continuing weakness in the job market. The four-week average of initial weekly claims will probably have to fall below 400,000 before the total employment stops falling.
Wednesday, September 09, 2009
Corus Bank: "The Great Enabler of Condo Madness"
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 09:12:00 PM
From Eric Dash at the NY Times: In Florida, Vestiges of the Boom
On the corner of Flamingo Road and Pink Flamingo Lane ... a soaring monument to the great condominium bust bakes under the Florida sun.This article touches on several key points - the speculative activities of Corus, the slow response of their primary regulator, the FDIC trying to split the bank in two to sell the banking operations (not worth much) separately from the "monuments to madness" condo towers (also not worth much), the coming losses from C&D and CRE loans for other banks, the coming hit from Corus to the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) and more ...
The Tao Sawgrass ... built on the western fringes of Fort Lauderdale with easy money from the now tottering condo king of American finance: Corus Bancshares of Chicago. Only about 50 of the 396 units have been sold.
... The primary regulator of Corus, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, failed to sound the alarm until Corus was deeply troubled. ... Corus will go down as the great enabler of condo madness, and its travails are a harbinger of the pain yet to come in the troubled world of commercial real estate.
...regulators are moving to cleave the bank in two and sell its banking operations and condominium loans separately. The hope is to clinch a deal by the end of the month.
Also, this article suggests Corus might have until the end of the month. However the bids for assets were due last Thursday, and I think it is likely that Corus will be seized this week.
Obama on Health Care
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 08:05:00 PM
YouTube live feed (ht bANK fAILURE) or Link Here for large image.
Note: Embed removed. Here is the text for the speech.
A comment on the Deficit and National Debt
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 07:21:00 PM
There seems to more and more concern about the deficit and the increases in the National Debt. It is definitely scary, and I've been writing about this issue for a number of years.
Back in late 2000 and in 2001 (I started this blog in January 2005) I focused on the deficit - and the long term fiscal damage I felt the Bush policies would cause.
President Bush argued in February 2001 that his fiscal policy "returns ... the surplus to the American taxpayers". In his 2001 testimony to Congress, then Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan supported President Bush by offering projections of "an on-budget surplus of almost $500 billion ... in fiscal year 2010". The National Debt would soon be retired and the Boomer's retirements secure. Greenspan offered a projection of "an implicit on-budget surplus under baseline assumptions well past 2030 despite the budgetary pressures from the aging of the baby-boom generation, especially on the major health programs."
Mr Bush also said in February 2001: "After paying the bills, my plan reduces the national debt, and fast. So fast, in fact, that economists worry that we're going to run out of debt to retire. That would be a good worry to have."
I disagreed strongly with President Bush and Mr. Greenspan's projections. I argued the surpluses were a mirage, and the tax policies would create a significant structural deficit.
I became even more adamant about the Bush structural deficits in 2004 and 2005, when it became obvious that the small improvement in the annual deficit was because of the housing bubble. I wrote in March 2005 about why I was so concerned about the housing bubble:
If we slide into a global recession, we have limited tools available to stimulate the economy. Interest rates are already very low (although the Fed has recently put some arrows back into the quiver), and we are already running general fund budget deficits of close to 6% of GDP.In 2006, Professor Samwick (who served as Chief Economist on the Staff of President Bush's Council of Economic Advisers) wrote: First Things First
CR writes:Today I believe some people are getting upset about the wrong thing at the wrong time. As Samwick noted, during a recession the deficits will increase - from falling tax revenues, automatic stabilizers and stimulus spending. Maybe some people disagree with the stimulus package, but that isn't going to change (except additions like extending unemployment benefits again).Everyone should agree that the most immediate fiscal problem is the structural General Fund deficit. Excluding future health care costs, the structural deficit is around 4% to 4.5% of GDP. This serious problem has been caused almost exclusively by Bush's policies. And imagine if the economy slows next year, as many people expect, adding a cyclical deficit on top of the huge Bush structural deficit.CR is correct in his diagnosis of the immediacy and the size of the problems of the General Fund deficit. As I have discussed in earlier posts ... the appropriate target for the General Fund deficit is for it to average to zero over a business cycle. A corollary to that is that the General Fund should be in surplus during the non-recessionary parts of that business cycle. (A slightly weaker target that I would also accept is that the Debt/GDP ratio not trend upward over time.)
So isn't it reasonable to suggest that Mr. Bush and the GOP fix the structural deficit first, before addressing other long-term issues? Of course.
Eliminating the recessionary deficit requires the economy to recover, and unfortunately the recovery will most likely be choppy and sluggish, but eventually a recovery will happen. Eliminating the structural deficit will be much more difficult and will require hard choices, but now is not the time.
The time to concerned about the structural deficit was in 2001 through 2006, and hopefully again starting in 2011 or 2012.
Market and StuyTown Update
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 04:08:00 PM
Since I haven't posted this in some time ... Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This graph is from Doug Short of dshort.com (financial planner): "Four Bad Bears".
Note that the Great Depression crash is based on the DOW; the three others are for the S&P 500.
And on StuyTown from the NY Times: Buyers of Huge Manhattan Complex Face Default Risk (ht Ann)
[T]he buyers [of Stuyvesant Town and Peter Cooper Village in Manhattan] are running out of time and money. Jerry and Rob Speyer and their partner, BlackRock Realty, who together paid $5.4 billion ... have nearly exhausted an additional $890 million set aside for apartment renovations, landscaping and interest payments. Rents are down 25 percent from their peak.At that valuation - about two-thirds off the total $6.3 billion price - the equity is wiped out, the mezzanine debt is wiped out, and the first mortgage will take a significant haircut.
Real estate analysts say that the partnership’s money will run out as soon as December and that the owners are at “high risk” of default on $4.4 billion in loans.
...
A recent report from Realpoint, a credit rating agency, estimates that the property has a value today of only $2.13 billion.
...
At Stuyvesant Town, there is a $3 billion first mortgage, or commercial mortgage-backed security, and a $1.4 billion second loan, known as “mezzanine debt” held by SL Green, the government of Singapore and others.
Finally, there is $1.9 billion in equity put up by Tishman Speyer, BlackRock and their investors.
Fed's Beige Book: Economic Activity Stabilizing
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 02:00:00 PM
From the Fed: Beige Book
Reports from the 12 Federal Reserve Districts indicate that economic activity continued to stabilize in July and August. Relative to the last report, Dallas indicated that economic activity had firmed, while Boston, Cleveland, Philadelphia, Richmond, and San Francisco mentioned signs of improvement. Atlanta, Chicago, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and New York generally described economic activity as stable or showing signs of stabilization; St. Louis remarked that the pace of decline appeared to be moderating. Most Districts noted that the outlook for economic activity among their business contacts remained cautiously positive.And on real estate:
The majority of Districts reported flat retail sales.
emphasis added
Residential real estate markets remained weak, but signs of improvement continued to be noted. Chicago, Richmond, Boston, and San Francisco observed an uptick in sales over the last six weeks, while sales in the Philadelphia District were described as steady. ... Most Districts noted that demand remained stronger at the low-end of the housing market. Boston, Cleveland, Dallas, Kansas City, Richmond, and New York indicated that the first-time home buyer tax incentive was spurring sales. However, Philadelphia did note an upturn in sales at the high-end of the market. Reports on house prices generally indicated ongoing downward pressures ...Stabilization is not new growth. Just more beige shoots ...
Reports on commercial real estate markets indicated that demand for space remained weak and that construction continued to decline in all Districts. Atlanta, Philadelphia, Richmond, and San Francisco reported that vacancy rates increased, while rates held steady in the Boston and Kansas City Districts and were mixed in New York. ... Commercial rents declined according to Boston, Chicago, New York, Philadelphia, and Richmond. Rent concessions were reported in the Richmond and San Francisco markets, and Richmond noted that some landlords had postponed property improvements in an effort to conserve cash. Construction remained at very low levels, with modest improvements noted in public construction in the Chicago, Cleveland, and Minneapolis Districts.
Mortgage Cram Downs: The Return
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 12:10:00 PM
From Ryan Grim at the HuffPost: Cramdown Is Back: Banks Against Homeowners, Round 2 (ht Atrios)
House Financial Services Committee Chairman Barney Frank (D-Mass.) tells the Huffington Post he plans to revive the effort to give bankruptcy judges the authority to renegotiate home mortgages -- by making it part of this fall's much-anticipated financial regulatory reform bill.For a history of mortgage Cram Downs, and why they are needed, see Tanta's Just Say Yes To Cram Downs . Some excerpts:
...
On Tuesday, Frank was asked by HuffPost if he had plans to readdress cramdown. "Yes, as I will announce tomorrow, and I told this to bankers, given the slow pace of modifications, for whatever reason: they're not putting enough people on it, they're not taking it seriously, there are legal obstacles. As of now my intention would be to include the bankruptcy on primary residences in the reg reform."
The prohibition of court-ordered modifications for mortgages on principal residences was created in 1978; between 1978 and 1993 most bankruptcy courts interpreted the law to mean that while interest-rate reduction or term-extension modifications were not allowed, home mortgages could still be crammed down.There is much more in Tanta's post.
In 1993, with Nobleman v. American Savings Bank, the Supreme Court held that the prohibition on modifications of principal-residence mortgage loans also included cram downs. The result is that borrowers who are upside down and who have toxic, high-rate mortgages are simply, in practical terms, unable to maintain their homes in Chapter 13.
...
I am fully in favor of removing restrictions on modifications of mortgage loans in Chapter 13, but not necessarily because that helps current borrowers out of a jam. I'm in favor of it because I think it will be part of a range of regulatory and legal changes that will help prevent future borrowers from getting into a lot of jams, which is to say that it will, contra MBA, actually help "stabilize" the residential mortgage market in the long term. Any industry that wants special treatment under the law because of the socially vital nature of its services needs to offer socially viable services, and since the industry has displayed no ability or willingness to quit partying on its own, then treat it like any other partier under BK law.
Cram downs are in important step: as Ryan Grim notes in the HuffPost article, the mortgage modification programs are all "carrot" and the cram downs will provide a "stick", and more importantly, as Tanta noted, the cram downs will bring discipline to the mortgage industry.
Treasury: Millions More Foreclosures Coming
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 10:58:00 AM
From Teasury: Assistant Secretary for Financial Institutions Michael S. Barr Written Testimony on Stabilizing the Housing Market before the House Financial Services Committee, Subcommittee on Housing and Community Opportunity
... I want to highlight some key points of success:It is that third category that is key - that is all the homeowners far underwater who bought homes they could never really afford.
We have signed contracts with over 45 servicers, including the five largest. Between loans covered by these servicers and loans owned or guaranteed by the GSEs, more than 85 percent of all mortgage loans in the country are now covered by the program.
Over 570,000 trial modifications have been offered under the program. Over 360,000 trial modifications are underway.
...
[W]e recognize that any modification program seeking to avoid preventable foreclosures has limits, HAMP included. Even before the current crisis, when home prices were climbing, there were still many hundreds of thousands of foreclosures. Therefore, even if HAMP is a total success, we should still expect millions of foreclosures, as President Obama noted when he launched the program in February.
Some of these foreclosures will result from borrowers who, as investors, do not qualify for the program. Others will occur because borrowers do not respond to our outreach. Still others will be the product of borrowers who bought homes well beyond what they could afford and so would be unable to make the monthly payment even on a modified loan.
emphasis added
Bankruptcies: Movin' on Up!
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 09:04:00 AM
From Bloomberg: Wealthy Families Succumb to Bankruptcy as Real Estate Crashes
Wealthy individuals’ Chapter 11 bankruptcy filings jumped 73 percent in the second quarter from a year earlier, according to the National Bankruptcy Research Center, a research firm in Burlingame, California.Overall personal bankruptcies were up 36% in Q2 2009 compared to Q2 2008 - so high end bankruptcies are increasing twice as fast as the average.
More individuals or families with at least $1,010,650 in secured debt and $336,900 unsecured are using Chapter 11 of the U.S. bankruptcy code typically associated with business reorganizations. Falling U.S. home prices leave them unable to refinance or sell properties when they drop below the value of the mortgage, said Chicago bankruptcy attorney Joseph Baldi.
... Wealthier people filing for bankruptcy typically have large homes, two car payments and children in private schools, said Leslie Linfield, executive director of the Institute for Financial Literacy in Portland, Maine ...
“There are a lot of people with real estate, and they can’t afford it,” said Baldi ... “They can’t make the payments, and they can’t sell the house.”
emphasis added
This fits with the articles yesterday on Option ARMs and Interest Only loans that were used predominantly in mid-to-high end areas.
Tuesday, September 08, 2009
Interest Only Loans: Another Time Bomb
by Calculated Risk on 9/08/2009 11:12:00 PM
From David Streitfeld at the NY Times: The House Trap
An analysis for The New York Times by the real estate information company First American CoreLogic shows there are 2.8 million active interest-only home loans worth a combined total of $908 billion.There are a several fascinating anecdotes in the article, including a professor who teaches real estate finance. Here is one:
The interest-only periods, which put off the principal payments for five, seven or 10 years, are now beginning to expire. In the next 12 months, $71 billion of interest-only loans will reset. The year after, another $100 billion will reset. After mid-2011, another $400 billion will reset.
“I understand I took a risk,” said [Dean Janis, a Southern California lawyer who bought a $950,000 home in 2004] “But I did not anticipate that the real estate market would go down 30 percent.” He talked with Wells Fargo about his options, and the lender said he had none.IOs. Another wonderful affordability product.
FHA Lenders with High Default Rates
by Calculated Risk on 9/08/2009 10:22:00 PM
HUD has a great tool to track FHA lender performance: Neighborhood Watch Early Warning System (ht TL)
Although the overall FHA default rate is 4.63%, the following lenders had 2 year default rates of 15% or more (only lenders with 100+ originations included). (Added: these are the two year default rates).
There are ten lenders with "perfect" records (100% default), but they only have one or two originations each.
And the winner is Mortgage Depot Inc. with a 48.65% default rate!
Note that Countrywide Home Loans Inc. is not Countrywide Bank FSB.
For a full screen version of the table click here.
The table is wide - use scroll bars to see all information!
NOTE: Columns are sortable - click on column header to sore
Fitch on Option ARM Recasts
by Calculated Risk on 9/08/2009 05:58:00 PM
From Fitch: $134B of U.S. Option ARM RMBS To Recast by 2011
Of the $189 billion securitized Option ARM loans outstanding, 88% have yet to experience a recast event ... Of these loans that have not yet recast, 94% have utilized the minimum monthly payment to allow their loans to negatively amortize.Fitch is just looking at securitized Option ARMs, not loans in bank portfolios like Wells Fargo with all the 10 year Pick-a-Pay recast periods.
...
Further evidence of option ARM underperformance in the last year lies in the number of outstanding securitized Option ARMs either 90 days or more delinquent, in foreclosure or real estate-owned proceedings, which has increased from 16% to 37%. Total 30+ day delinquencies are now 46%, despite the fact that only 12% have recast and experienced an associated payment shock. Instead, negative and declining equity has presented a larger problem: due to high concentrations in California, Florida, and other states with rapidly declining home prices, average loan-to-value ratios have increased from 79% at origination to 126% today. 'Negative equity and payment shocks will continue as Option ARM loans recast in large numbers in the coming years,' said Somerville.
The second paragraph is key - many of these borrowers are defaulting before the loans recast! From Bloomberg on a Barclays report in July: Option ARM Defaults Shrink Recast Wave, Barclays Says
The wave of “option” adjustable- rate mortgages recasting to higher payments, projected by some economists to represent a looming source of foreclosures that will hurt housing markets over the next few years, will be smaller “than feared” because many borrowers will default before their bills change, Barclays Capital analysts said.The real problem for Option ARMs is negative equity, and the surge in defaults is happening before the loans recast. As Fitch notes, modifications haven't been helpful for Option ARM borrowers because many are too far underwater:
...
About 40 percent of borrowers with option ARMs are already delinquent, and “many” of the others will start missing payments before their obligations change, the Barclays mortgage- bond analysts wrote in a July 24 report. ...
“The additional risk really will only be for borrowers who manage to stay current over the next couple of years and might default due to a payment shock,” the New York-based analysts including Sandeep Bordian and Jasraj Vaidya wrote.
...
More than $750 billion of option ARMs were originated between 2004 and 2008 ...
To date, 3.5% of the approximately one million 2004-2007 vintage securitized Option ARM loans have been modified, in an attempt to mitigate effects from the payment shock. Modification types have included term extension, conversion to interest only loans, interest rate cuts, and others. These modifications have been somewhat successful, with 24% of modified Option ARM loans being 90+ days delinquent, compared with 37% of the overall Option ARM universe. However ... Fitch expects a high default percentage for modified Option ARM loans.This is a somewhat confusing press release. The recasts will probably lead to higher defaults, but negative equity is the real problem.
Consumer Credit Declines Sharply in July
by Calculated Risk on 9/08/2009 03:10:00 PM
From MarketWatch: U.S. consumer credit down record amount in July
UU.S. consumers reduced their credit burden by a record amount in July, the Federal Reserve reported Tuesday. Total seasonally adjusted consumer debt fell $21.55 billion, or at a 10.4% annual rate, in July to $2.47 trillion. This is the sixth straight monthly drop in consumer credit. ... This is the record 11th straight monthly drop in credit card debt.
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.This graph shows the year-over-year (YoY) change in consumer credit. Consumer credit is off 4.2% over the last 12 months. The previous record YoY decline was 1.9% in 1991.
Here is the Fed report: Consumer Credit
Consumer credit declined from $2,493.6 billion in June to $2,472.1 in July. Note: The Fed reports a simple annual rate (multiplies change in month by 12) as opposed to a compounded annual rate.
Note: Consumer credit does not include real estate debt.
Seasonal Retail Hiring
by Calculated Risk on 9/08/2009 02:33:00 PM
Typically retail companies start hiring for the holiday season in October, and really increase hiring in November. Here is a graph that shows the historical net retail jobs added for October, November and December by year. Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This really shows the collapse in retail hiring in 2008. This also shows how the season has changed over time - back in the '80s, retailers hired mostly in December. Now the peak month is November, and many retailers start hiring seasonal workers in October.
Here is a story from Bloomberg: Retail Hiring Shift May Show Growing Confidence in Recovery (ht Brian, Mike)
U.S. discount, grocery and restaurant chains are hiring a larger percentage of job applicants than seven months ago, signaling confidence the economy may be improving, software maker Kronos Inc. said.Unfortunately this data is new and the season hasn't started yet. This hiring will be watched closely, and I suspect seasonal hiring will be stronger than in 2008, but not as strong as the 700+ thousand jobs in 2004 through 2007.
Kronos analyzed the 8.9 million job applications received by 68 retailers in the first seven months of the year. In July, 2.99 of every 100 applications resulted in a hire, compared with 2.75 in January, a three-year low, the Chelmsford, Massachusetts-based company said today in a statement.
“We are seeing a turnaround that reflects an increase in confidence by individual managers,” Robert Yerex, Kronos’s chief economist ... “It may take quite a bit longer to come back than it did to drop off.” This is the first time Kronos has publicly issued a monthly retail labor index.
Google Domestic Trends
by Calculated Risk on 9/08/2009 12:46:00 PM
Here is an interesting resource from Google: Domestic Trends. (ht Brian) Google is tracking search trends for several specific sectors of the economy.
As an example, below is a screen capture of the Auto Buyers Index.  Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This shows the seasonality of car buying, plus the Cash-for-clunkers surge in searches. Click on link for interactive graph - you can also plot the data YoY.
I also recommend real estate, rental (still weak) and unemployment.


