by Calculated Risk on 8/23/2012 09:04:00 PM
Thursday, August 23, 2012
Friday: Durable Goods, Europe, and requesting a favor
First, my friend Tom Lawler has been very kind and allowed me to excerpt pieces from his daily newsletter to share with everyone. The Lawler's beloved horse "Dealer" has had some lameness issues this year, and to cheer up his wife (and himself) Tom entered Dealer in a local best pet contest and hopes to surprise his wife with "Dealer" being named best pet. Right now Dealer is trailing in the voting, and Tom needs your help. If you could spare a few seconds, please go to this site and vote for "Dealer". Thank you so much!
A few articles on global issues ...
From the NY Times: French and German Leaders Meet as Fresh Signs Point to Regional Recession
Returning to business after their summer breaks, the German and French leaders met here Thursday to discuss the continuing crisis in the euro zone, even as fresh economic data reinforced fears that the region was sliding into recession.From the NY Times: China Confronts Mounting Piles Of Unsold Goods
After three decades of torrid growth, China is encountering an unfamiliar problem with its newly struggling economy: a huge buildup of unsold goods that is cluttering shop floors, clogging car dealerships and filling factory warehouses.From the Financial Times: Athens and Berlin in spat over funds
The glut of everything from steel and household appliances to cars and apartments is hampering China’s efforts to emerge from a sharp economic slowdown. It has also produced a series of price wars and has led manufacturers to redouble efforts to export what they cannot sell at home.
Leaders in Athens and Berlin wrangled publicly over how to deal with Greece’s plea for further assistance as fears of a renewed eurozone recession mounted yesterday.On Friday:
...
Wolfgang Schäuble, finance minister, said on German radio that there was “understanding” for Athens’ predicament, but giving it more time was “not the solution”, adding: “More time implies . . . more money.”
excerpt with permission
• At 8:30 AM ET, Durable Goods Orders for July from the Census Bureau. The consensus is for a 1.9% increase in durable goods orders.
• At 10:00 AM, the Worker Displacement report from the BLS for January 2012 will be released. This report will probably receive some attention because of weak labor market.
• Europe Note: the Spanish Government is expected to announce the details of the bank bailout. Also on Friday, Greek Prime Minister Samaras and German Chancellor Merkel will meet in Berlin with a press conference to follow.
Earlier:
• New Home Sales increase in July to 372,000 Annual Rate
• New Home Sales and Distressing Gap
• New Home Sales graphs
Misc: Negative Equity declines, FHFA house prices increase, Flash PMI
by Calculated Risk on 8/23/2012 04:44:00 PM
• From Zillow: Negative Equity Falls in Second Quarter; Nearly Half of Borrowers Under 40 Remain Underwater
Negative equity declined in the second quarter, with 30.9 percent of U.S. homeowners with mortgages – or 15.3 million – underwater, according to the second quarter Zillow® Negative Equity Report. That was down from 31.4 percent of homeowners with mortgages, or 15.7 million, underwater in the first quarter.That is a decline of about 400,000 borrowers (I expect a larger decline when CoreLogic reports). Zillow chief economist Stan Humphries has more: Negative Equity Declines Slightly on the Back of Modest Home Value Gains
The total amount of negative equity in the country declined by $42 billion in the second quarter to $1.15 trillion.
While roughly one out of every three homeowners with mortgages is underwater, 91 percent of these homeowners are current on their mortgage and continue to make payments.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Humphries provided this chart of Zillow's estimate of the Loan-to-Value (LTV) for homeowners with a mortgage. From Humphries:
Over 40 percent of underwater homeowners (12.5 percent of all homeowners with a mortgage), owe between 1 and 20 percent more than their home is worth. On the other end of the spectrum, about 2.2 million underwater homeowners (4.5 percent of all homeowners with mortgages) owe more than double what their home is worthThe biggest concern are those homeowners deep underwater.
• From the FHFA: U.S. House Prices Rose 1.8 Percent From First Quarter to Second Quarter 2012
U.S. house prices rose 1.8 percent from the first quarter to the second quarter of 2012 according to the Federal Housing Finance Agency’s (FHFA) seasonally adjusted purchase-only house price index (HPI). The HPI is calculated using home sales price information from Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac mortgages. Seasonally adjusted house prices rose 3.0 percent from the second quarter of 2011 to the second quarter of 2012. FHFA’s seasonally adjusted monthly index for June was up 0.7 percent from May.The Case-Shiller index will for June will be released this coming Tuesday.
“Although some housing markets are still facing significant challenges, house prices were quite strong in most areas in the second quarter,” said FHFA Principal Economist Andrew Leventis. “The strong appreciation may partially reflect fewer homes sold in distress, but declining mortgage rates and a modest supply of homes available for sale likely account for most of the price increase.”
• From MarkIt: PMI continues to signal weak manufacturing expansion in August
The preliminary ‘flash’ PMI reading which is based on around 85% of usual monthly replies rose slightly from 51.4 in July to 51.9 ... Employment in the manufacturing sector rose further in August, but the rate of job creation slowed for the fifth month running to the weakest since December 2010.This was weak, but better than the expected 51.0.
Earlier:
• New Home Sales increase in July to 372,000 Annual Rate
• New Home Sales and Distressing Gap
• New Home Sales graphs
New Home Sales and Distressing Gap
by Calculated Risk on 8/23/2012 12:59:00 PM
As I mentioned earlier, new home sales have averaged 360,000 on an annual rate basis through July. That means sales are on pace to increase 18% from last year (I expect some upward revisions, and for sales to increase 20%+ this year).
Here is a table showing sales and the change from the previous year since the peak in 2005:
| Year | New Home Sales (000s) | Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 1,283 | |
| 2006 | 1,051 | -18% |
| 2007 | 776 | -26% |
| 2008 | 485 | -38% |
| 2009 | 375 | -23% |
| 2010 | 323 | -14% |
| 2011 | 306 | -5% |
| 20121 | 360 | 18% |
| 12012 pace through July. | ||
This is still a very low level of sales, but clearly new home sales have bottomed and are starting to recover. I don't expect sales to increase to 2005 levels, but something close to 800,000 is possible once the number of distressed sales declines to more normal levels.
Here is an update to the distressing gap graph.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This "distressing gap" graph that shows existing home sales (left axis) and new home sales (right axis) through June. This graph starts in 1994, but the relationship has been fairly steady back to the '60s.
Following the housing bubble and bust, the "distressing gap" appeared mostly because of distressed sales. The flood of distressed sales has kept existing home sales elevated, and depressed new home sales since builders haven't been able to compete with the low prices of all the foreclosed properties.
I don't expect much of an increase in existing home sales (distressed sales will slowly decline and be offset by more conventional sales). But I do expect this gap to close - mostly from an increase in new home sales.
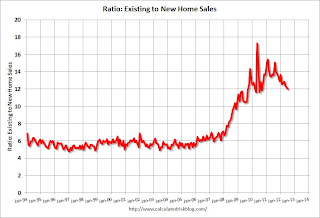 Another way to look at the same data is as a ratio of existing to new home sales. Historically this ratio has been around 6 (six times as many existing homes sold as new homes sold). I expect this ratio to tend back towards six over the next several years.
Another way to look at the same data is as a ratio of existing to new home sales. Historically this ratio has been around 6 (six times as many existing homes sold as new homes sold). I expect this ratio to tend back towards six over the next several years.Note: Existing home sales are counted when transactions are closed, and new home sales are counted when contracts are signed. So the timing of sales is different.
Earlier:
• New Home Sales increase in July to 372,000 Annual Rate
• New Home Sales graphs
New Home Sales increase in July to 372,000 Annual Rate
by Calculated Risk on 8/23/2012 10:00:00 AM
The Census Bureau reports New Home Sales in July were at a seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of 372 thousand. This was up from a revised 359 thousand SAAR in June (revised up from 350 thousand). Sales in May were revised down.
The first graph shows New Home Sales vs. recessions since 1963. The dashed line is the current sales rate.
Sales of new single-family houses in July 2012 were at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 372,000 ... This is 3.6 percent above the revised June rate of 359,000 and is 25.3 percent above the July 2011 estimate of 297,000.
 Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.
Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.The second graph shows New Home Months of Supply.
Months of supply declined to 4.6 in July from 4.8 in June.
The all time record was 12.1 months of supply in January 2009.
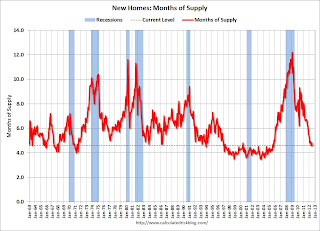 This is now in the normal range (less than 6 months supply is normal).
This is now in the normal range (less than 6 months supply is normal).The seasonally adjusted estimate of new houses for sale at the end of July was 142,000. This represents a supply of 4.6 months at the current sales rate.On inventory, according to the Census Bureau:
"A house is considered for sale when a permit to build has been issued in permit-issuing places or work has begun on the footings or foundation in nonpermit areas and a sales contract has not been signed nor a deposit accepted."Starting in 1973 the Census Bureau broke this down into three categories: Not Started, Under Construction, and Completed.
 This graph shows the three categories of inventory starting in 1973.
This graph shows the three categories of inventory starting in 1973.The inventory of completed homes for sale was at a record low 38,000 units in July. The combined total of completed and under construction is at the lowest level since this series started.
The last graph shows sales NSA (monthly sales, not seasonally adjusted annual rate).
In July 2012 (red column), 34 thousand new homes were sold (NSA). Last year only 27 thousand homes were sold in July. This was the fourth weakest July since this data has been tracked. The high for July was 117 thousand in 2005.
 Even though sales are still very low, new home sales have clearly bottomed. New home sales have averaged 360 thousand SAAR over the first 7 months of 2012, after averaging under 300 thousand for the previous 18 months. Most of the recent revisions have been up too.
Even though sales are still very low, new home sales have clearly bottomed. New home sales have averaged 360 thousand SAAR over the first 7 months of 2012, after averaging under 300 thousand for the previous 18 months. Most of the recent revisions have been up too.This was another fairly solid report and indicates an ongoing sluggish recovery in residential investment.
Weekly Initial Unemployment Claims increase to 372,000
by Calculated Risk on 8/23/2012 08:30:00 AM
The DOL reports:
In the week ending August 18, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 372,000, an increase of 4,000 from the previous week's revised figure of 368,000. The 4-week moving average was 368,000, an increase of 3,750 from the previous week's revised average of 364,250.The following graph shows the 4-week moving average of weekly claims since January 2000.

Click on graph for larger image.
The dashed line on the graph is the current 4-week average. The four-week average of weekly unemployment claims increased to 368,000.
This was above the consensus forecast of 365,000.
 And here is a long term graph of weekly claims:
And here is a long term graph of weekly claims:The 4-week average post-bubble low is 363,000; this week the average was at 368,000.
Wednesday, August 22, 2012
Thursday: New Home Sales, Weekly Unemployment Claims
by Calculated Risk on 8/22/2012 08:41:00 PM
From Jon Hilsenrath and Kristina Peterson at the WSJ: Fed Moving Closer to Action
The Federal Reserve sent its strongest signal yet that it is preparing new steps to bolster the economic recovery, saying measures would be needed fairly soon unless growth substantially and convincingly picks up.Here is Tim Duy's take: It's All About The Data
Lots of possibilities at this point. If you were looking for additional asset purchases at the last FOMC meeting, you were not crazy. There was obviously widespread concern about the mid-year slowdown and its implications for the stability of the Fed's forecasts. Moreover, policymakers appear to have concluded that additional asset purchases could be effective. If the data had continued to progress as it had since the July/August meeting, I would say that another round of QE was a slam-dunk. But the data has not progressed in the same direction; rather than falling short of expectations, it has tended toward upside surprises. That of course could change over the next few weeks. In short, we need to ask ourselves what will constitute a "substantial and sustainable strengthening." If Lockhart is a guide, I am thinking we have seen such a shift already. If so, I would expect that on the basis of current data the Fed would delay action until closer to the end of Operation Twist II and to see if Congress has come to any agreement on the fiscal situation in 2013. If the change in the data has not reached the threshold of "substantial and sustainable strengthening" then we would expect action. It will be interesting to see if any of the doves back off on their dreary forecasts in the coming days; such shifts in tone would be telling. Also note that there is a middle ground in the possibility of further changes to the communication strategy; something that could placate both the doves and the hawks until a clearer image of the path of the US economy emerges.On Thursday:
• At 8:30 AM ET, the initial weekly unemployment claims report will be released. The consensus is for claims to decrease to 365 thousand from 366 thousand.
• At 9:00 AM, the Markit US PMI Manufacturing Index Flash. This is a new release and might provide hints about the ISM PMI for August. The consensus is for a reading of 51.0, down from 51.8 in July.
• At 10:00 AM, New Home Sales for July will be released by the Census Bureau. The consensus is for an increase in sales to 362 thousand Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate (SAAR) in July from 350 thousand in June. Watch for upgrades to the sales rate for previous months.
• Alst at 10:00 AM, the FHFA House Price Index for June 2012 will be released. This is based on GSE repeat sales and the consensus is for a 0.6% increase in house prices.
Another question for the monthly economic prediction contest:
Europe Note: German Chancellor Merkel and French President Hollande will meet in Berlin
AIA: Architecture Billings Index Downturn Moderates as Negative Conditions Continue in July
by Calculated Risk on 8/22/2012 04:02:00 PM
Note: This index is a leading indicator primarily for new Commercial Real Estate (CRE) investment.
From AIA: Architecture Billings Index Downturn Moderates as Negative Conditions Continue
The Architecture Billings Index (ABI) pointed to a slower decline in July in design activity at U.S. architecture firms. As a leading economic indicator of construction activity, the ABI reflects the approximate nine to twelve month lag time between architecture billings and construction spending. The American Institute of Architects (AIA) reported the July ABI score was 48.7, up considerably from the mark of 45.9 in June. This score reflects a decrease in demand for design services (any score below50 indicates a decline in billings). The new projects inquiry index was 56.3, up from mark of 54.4 the previous month.
“Even though architecture firm billings nationally were down again in July, the downturn moderated substantially,” said AIA Chief Economist, Kermit Baker, PhD, Hon. AIA. “As long as overall economic conditions continue to show improvement, modest declines should shift over to growth in design activity over the coming months.”
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the Architecture Billings Index since 1996. The index was at 48.7 in July, up from 45.9 in June. Anything below 50 indicates contraction in demand for architects' services.
Note: This includes commercial and industrial facilities like hotels and office buildings, multi-family residential, as well as schools, hospitals and other institutions.
According to the AIA, there is an "approximate nine to twelve month lag time between architecture billings and construction spending" on non-residential construction. This suggests further weakness in CRE investment later this year and into next year (it will be some time before investment in offices and malls increases).
Earlier on existing home sales:
• Existing Home Sales in July: 4.47 million SAAR, 6.4 months of supply
• Existing Home Sales: Inventory and NSA Sales Graph
• Existing Home Sales graphs
FOMC Minutes: Discussion of policy tools the FOMC "might employ"
by Calculated Risk on 8/22/2012 02:00:00 PM
Update: Here is a key sentence:
"Many members judged that additional monetary accommodation would likely be warranted fairly soon unless incoming information pointed to a substantial and sustainable strengthening in the pace of the economic recovery"From the Fed: Minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee, July 31-August 1, 2012. Excerpt:
Participants discussed a number of policy tools that the Committee might employ if it decided to provide additional monetary accommodation to support a stronger economic recovery in a context of price stability. One of the policy options discussed was an extension of the period over which the Committee expected to maintain its target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent. It was noted that such an extension might be particularly effective if done in conjunction with a statement indicating that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy was likely to be maintained even as the recovery progressed. Given the uncertainty attending the economic outlook, a few participants questioned whether the conditionality of the forward guidance was sufficiently clear, and they suggested that the Committee should consider replacing the calendar date with guidance that was linked more directly to the economic factors that the Committee would consider in deciding to raise its target for the federal funds rate, or omit the forward guidance language entirely.This seems to suggest that "many participants" are supportive of QE3, although an alternative might be an extension of the period of exceptionally low rates.
Participants also exchanged views on the likely benefits and costs of a new large-scale asset purchase program. Many participants expected that such a program could provide additional support for the economic recovery both by putting downward pressure on longer-term interest rates and by contributing to easier financial conditions more broadly. In addition, some participants noted that a new program might boost business and consumer confidence and reinforce the Committee's commitment to making sustained progress toward its mandated objectives. Participants also discussed the merits of purchases of Treasury securities relative to agency MBS. However, others questioned the possible efficacy of such a program under present circumstances, and a couple suggested that the effects on economic activity might be transitory. In reviewing the costs that such a program might entail, some participants expressed concerns about the effects of additional asset purchases on trading conditions in markets related to Treasury securities and agency MBS, but others agreed with the staff's analysis showing substantial capacity for additional purchases without disrupting market functioning. Several worried that additional purchases might alter the process of normalizing the Federal Reserve's balance sheet when the time came to begin removing accommodation. A few participants were concerned that an extended period of accommodation or an additional large-scale asset purchase program could increase the risks to financial stability or lead to a rise in longer-term inflation expectations. Many participants indicated that any new purchase program should be sufficiently flexible to allow adjustments, as needed, in response to economic developments or to changes in the Committee's assessment of the efficacy and costs of the program.
Some participants commented on other possible tools for adding policy accommodation, including a reduction in the interest rate paid on required and excess reserve balances. While a couple of participants favored such a reduction, several others raised concerns about possible adverse effects on money markets. It was noted that the ECB's recent cut in its deposit rate to zero provided an opportunity to learn more about the possible consequences for market functioning of such a move. In light of the Bank of England's Funding for Lending Scheme, a couple of participants expressed interest in exploring possible programs aimed at encouraging bank lending to households and firms, although the importance of institutional differences between the two countries was noted.
Existing Home Sales: Inventory and NSA Sales Graph
by Calculated Risk on 8/22/2012 11:42:00 AM
The NAR had some issues with the report this morning. Here is the press release: Existing-Home Sales Improve in July, Prices Continue to Rise
Total existing-home sales, which are completed transactions that include single-family homes, townhomes, condominiums and co-ops, grew 2.3 percent to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 4.47 million in July from 4.37 million in June, and are 10.4 percent above the 4.05 million-unit pace in July 2011.Based on historical turnover rates, I think "normal" sales would be in the 4.5 to 5.0 million range. So existing home sales are close to "normal" now, however, of course, "normal" would have very few distressed sales - so in that sense the market is a long ways from "normal". But no one should expect existing home sales to go back to 6 or 7 million per year. Instead the key to returning to "normal" is more conventional sales and fewer distressed sales.
...
Total housing inventory at the end July increased 1.3 percent to 2.40 million existing homes available for sale, which represents a 6.4-month supply at the current sales pace, down from a 6.5-month supply in June. Listed inventory is 23.8 percent below a year ago when there was a 9.3-month supply.
...
Distressed homes – foreclosures and short sales sold at deep discounts – accounted for 24 percent of July sales (12 percent were foreclosures and 12 percent were short sales), down from 25 percent in June and 29 percent in July 2011.
...
Given population and demographic demand, [Lawrence Yun, NAR chief economist] said existing-home sales could be in a normal range of 5 to 5.5 million if all conditions were optimal. “Sales may reach 5 million next year, but it will require more sensible lending standards and stronger job creation to push beyond that,” he said.
As I've noted before, what matters the most in the NAR's existing home sales report is inventory; and what matters the most in the new home sales report tomorrow is sales. It is active inventory that impacts prices (although the "shadow" inventory will keep prices from rising). Those looking at the number of existing home sales for a recovery in housing are looking at the wrong number. For existing home sales, look at inventory first and then at the percent of conventional sales.
The NAR reported inventory increased to 2.40 million units in July, up slightly from June. This is down 23.8% from July 2011, and down 13% from the inventory level in July 2005 (mid-2005 was when inventory started increasing sharply). This is the same level for inventory as in July 2004.
Clearly inventory will be below the comparable month in 2005 for the rest of the year and will probably track close to the level in 2004. It looks like inventory peaked this year in April.
Important: The NAR reports active listings, and although there is some variability across the country in what is considered active, most "contingent short sales" are not included. "Contingent short sales" are strange listings since the listings were frequently NEVER on the market (they were listed as contingent), and they hang around for a long time - they are probably more closely related to shadow inventory than active inventory. However when we compare inventory to 2005, we need to remember there were no "short sale contingent" listings in 2005. In the areas I track, the number of "short sale contingent" listings is also down sharply year-over-year.
The following graph shows inventory by month since 2004. In 2005 (dark blue columns), inventory kept rising all year - and that was a clear sign that the housing bubble was ending.
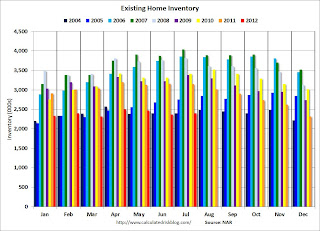 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This year (dark red for 2012) inventory is at the lowest level for the month of July since 2004, and inventory is below the level in July 2005 (not counting contingent sales). However inventory is still elevated using months-of-supply, but I expect months-of-supply to be below 6 later this year.
The following graph shows existing home sales Not Seasonally Adjusted (NSA).
 Sales NSA (red column) are above the sales for 2008, 2010 and 2011. Sales are well below the bubble years of 2005 and 2006.
Sales NSA (red column) are above the sales for 2008, 2010 and 2011. Sales are well below the bubble years of 2005 and 2006.Earlier:
• Existing Home Sales in July: 4.47 million SAAR, 6.4 months of supply99
• Existing Home Sales graphs
Existing Home Sales in July: 4.47 million SAAR, 6.4 months of supply
by Calculated Risk on 8/22/2012 10:00:00 AM
Note: The NAR had release issues this morning.
From the WSJ: Home Resales Jump
Existing-home sales increased 2.3% in July from a month earlier to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 4.47 million, the National Association of Realtors said Wednesday. The month's sales were 10.4% above the same month a year earlier.
The sales pace for June was unrevised at 4.37 million per year.
The median sales price in July, meanwhile, was $187,300, up 9.4% from the same month a year earlier and the strongest year-over year gain since January 2006.
At the end of July, meanwhile, the inventory of previously owned homes listed for sale rose 1.3% to 2.4 million. That represented a 6.4 month supply at the current sales pace
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows existing home sales, on a Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate (SAAR) basis since 1993.
Sales in July 2012 (4.47 million SAAR) were 2.3% higher than last month, and were 10.4% above the July 2011 rate.
The second graph shows nationwide inventory for existing homes.
 According to the NAR, inventory increased to 2.4 million in July from 2.39 million in June. Inventory is not seasonally adjusted, and usually inventory increases from the seasonal lows in December and January to the seasonal high in mid-summer.
According to the NAR, inventory increased to 2.4 million in July from 2.39 million in June. Inventory is not seasonally adjusted, and usually inventory increases from the seasonal lows in December and January to the seasonal high in mid-summer.The last graph shows the year-over-year (YoY) change in reported existing home inventory and months-of-supply. Since inventory is not seasonally adjusted, it really helps to look at the YoY change. Note: Months-of-supply is based on the seasonally adjusted sales and not seasonally adjusted inventory.
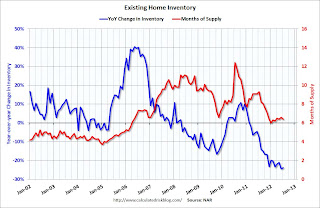 Inventory decreased 23% year-over-year in July from July 2011. This is the seventeenth consecutive month with a YoY decrease in inventory, and near the largest year-over-year decline reported.
Inventory decreased 23% year-over-year in July from July 2011. This is the seventeenth consecutive month with a YoY decrease in inventory, and near the largest year-over-year decline reported.Months of supply decreased to 6.4 months in July.
This was slightly below expectations of sales of 4.50 million. However, as I've noted before, those focusing on sales of existing homes, looking for a recovery for housing, are looking at the wrong number. For existing home sales, the key number is inventory - and the sharp year-over-year decline in inventory is a positive for housing. I'll have more later ...
MBA: Mortgage Refinance Activity declines as Rates Increase
by Calculated Risk on 8/22/2012 07:01:00 AM
From the MBA: Refinance Applications Decline as Rates Increase
The Refinance Index decreased 9 percent from the previous week to the lowest level since early July. The seasonally adjusted Purchase Index increased 0.9 percent from one week earlier.
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages with conforming loan balances ($417,500 or less) increased to 3.86 percent from 3.76 percent, with points decreasing to 0.42 from 0.47 (including the origination fee) for 80 percent loan-to-value ratio (LTV) loans.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph shows the MBA mortgage purchase index. The purchase index has been mostly moving sideways over the last two years.
Note: Yesterday Zillow reported "The 30-year fixed mortgage rate on Zillow(R) Mortgage Marketplace is currently 3.5 percent, up eight basis points from 3.42 percent at this same time last week."
 The second graph shows the refinance index.
The second graph shows the refinance index.The refinance activity has declined for three straight weeks as mortgage rates have moved higher. This is still a fairly high level of activity.
Tuesday, August 21, 2012
Wednesday: July Existing Home Sales, FOMC Minutes
by Calculated Risk on 8/21/2012 09:07:00 PM
Europe is coming back from vacation, from the WSJ: Europe Pressures Intensify
After a summer lull, Greece is again Ms. Merkel's biggest headache.Merkel and Samaras will meet on Friday with a press conference following ... The following week ECB President Mario Draghi will speak at the Jackson Hole Economic Symposium on Saturday, Sept 1st at 10 AM.
The Greek government, struggling with depression-like conditions that have pushed the economy to the brink, is likely to need many billions of euros of additional aid to avoid bankruptcy.
... The chancellor is set to meet with French President François Hollande on Thursday and Greek Prime Minister Antonis Samaras on Friday, meetings the chancellor's aides say will help determine Berlin's course.
... The chancellor isn't likely to reach a decision for several weeks, German officials said. In part, they said, she is waiting for two developments that could expand or constrain her options: Germany's constitutional court is due to rule on Sept. 12 on whether the euro zone can launch its permanent bailout fund, and inspectors from the European Union and the IMF are due to report on the size of Greece's finance shortfall. The latter could take until October, some euro-zone officials say.
On Wednesday:
• At 7:00 AM ET, the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) will release the mortgage purchase applications index.
• At 10:00 AM, Existing Home Sales for July is scheduled for release by the National Association of Realtors (NAR). The consensus is for sales of 4.50 million on seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) basis. Sales in June 2012 were 4.37 million SAAR.
• At 2:00 PM, the FOMC Minutes for the meeting of July 31-August 1, 2012 will be released. Once again the minutes will be closely scrutinized for hints about QE3.
Another question for the monthly economic prediction contest:
• During the day: The AIA's Architecture Billings Index for July (a leading indicator for commercial real estate) will be released.
FHFA: New Short Sale Guidelines for Fannie and Freddie
by Calculated Risk on 8/21/2012 05:10:00 PM
From the FHFA: New Standard Short Sale Guidelines for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac
The Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) today announced that Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are issuing new, clear guidelines to their mortgage servicers that will align and consolidate existing short sales programs into one standard short sale program. The streamlined program rules will enable lenders and servicers to quickly and easily qualify eligible borrowers for a short sale.A few details:
The new guidelines, which go into effect Nov. 1, 2012, will permit a homeowner with a Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac mortgage to sell their home in a short sale even if they are current on their mortgage if they have an eligible hardship. Servicers will be able to expedite processing a short sale for borrowers with hardships such as death of a borrower or co-borrower, divorce, disability, or relocation for a job without any additional approval from Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac.
“These new guidelines demonstrate FHFA’s and Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s commitment to enhancing and streamlining processes to avoid foreclosure and stabilize communities,” said FHFA Acting Director Edward J. DeMarco. “The new standard short sale program will also provide relief to those underwater borrowers who need to relocate more than 50 miles for a job.”
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac will waive the right to pursue deficiency judgments in exchange for a financial contribution when a borrower has sufficient income or assets to make cash contributions or sign promissory notes: Servicers will evaluate borrowers for additional capacity to cover the shortfall between the outstanding loan balance and the property sales price as part of approving the short sale.Short sales are already more common than foreclosures in many areas, and these new guidelines will probably lead to an even higher percentage of short sales next year (compared to foreclosures).
Offer special treatment for military personnel with Permanent Change of Station (PCS) orders: Service members who are being relocated will be automatically eligible for short sales, even if they are current on their existing mortgages, and will be under no obligation to contribute funds to cover the shortfall between the outstanding loan balance and the sales price on their homes.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac will offer up to $6,000 to second lien holders to expedite a short sale. Previously, second lien holders could slow down the short sale process by negotiating for higher amounts.
More from Fannie Mae: Fannie Mae Announces New Short Sale Guidelines
Under the new guidelines, servicers will be permitted to approve a short sale for borrowers who have certain hardships but have not yet gone into default. Those hardships include the death of a borrower or co-borrower, divorce or legal separation, illness or disability or a distant employment transfer. In addition, Fannie Mae is significantly reducing the documentation required to complete a short sale, including requiring no documentation of a borrower’s hardship 90 days or more delinquent and have a credit score lower than 620. This will remove barriers for those homeowners who are most in danger of foreclosure and increase servicer efficiency in completing a short sale.
Fannie Mae will also limit subordinate-lien payments to $6,000. Previously, subordinate lien holders often attempted to negotiate higher payments. The servicer will be able to offer the maximum payment of $6,000 in order to facilitate the transaction. By setting a standard payout amount and a limit for every transaction, Fannie Mae is removing the guess work and standardizing the transaction to help accelerate the short sale process.
... Fannie Mae completed 38,717 short sales through the first six months of 2012 and 70,025 in full year 2011.
Mortgage Delinquencies by State: Range and Current
by Calculated Risk on 8/21/2012 01:06:00 PM
Two weeks ago I posted a graph of mortgage delinquencies by state. This raised a question of how the current delinquency rate compares to before the crisis - and also a comparison to the peak of the delinquency crisis in each state.
The following graph shows the range of percent seriously delinquent and in-foreclosure for each state (dashed blue line) since 2007. The red diamond indicates the current serious delinquency rate (this includes 90+ days delinquent or in the foreclosure process).
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
Many states have seen declines, and several states have seen significant declines in the serious delinquency rate including Arizona, Michigan, Nevada and California. Other states, like New Jersey and New York, have made little or no progress in reducing serious delinquencies.
Arizona, Michigan, Nevada and California are all non-judicial foreclosure states. States with little progress like New Jersey and New York are judicial states. Florida is a judicial states - and has the highest serious deliquency rate - but Florida has seen some improvement.
 The second graph shows total delinquencies (including less than 90 days) and in-foreclosure.
The second graph shows total delinquencies (including less than 90 days) and in-foreclosure.
Although some states have seen significant declines in delinquency rates, all states are still above the Q1 2007 levels - and some states have seen little progress.
Philly Fed: State Coincident Indexes in July show weakness
by Calculated Risk on 8/21/2012 10:17:00 AM
From the Philly Fed:
The Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia has released the coincident indexes for the 50 states for July 2012. In the past month, the indexes increased in 22 states, decreased in 17, and remained stable in 11, for a one-month diffusion index of 10. Over the past three months, the indexes increased in 32 states, decreased in 14, and remained stable in four, for a three-month diffusion index of 36.Note: These are coincident indexes constructed from state employment data. From the Philly Fed:
The coincident indexes combine four state-level indicators to summarize current economic conditions in a single statistic. The four state-level variables in each coincident index are nonfarm payroll employment, average hours worked in manufacturing, the unemployment rate, and wage and salary disbursements deflated by the consumer price index (U.S. city average). The trend for each state’s index is set to the trend of its gross domestic product (GDP), so long-term growth in the state’s index matches long-term growth in its GDP.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This is a graph is of the number of states with one month increasing activity according to the Philly Fed. This graph includes states with minor increases (the Philly Fed lists as unchanged).
In July, 30 states had increasing activity, down from 35 in June. The last three months have been weak following eight months of widespread growth geographically. The number of states with increasing activity is at the lowest level since January 2010.
 Here is a map of the three month change in the Philly Fed state coincident indicators. This map was all red during the worst of the recession.
Here is a map of the three month change in the Philly Fed state coincident indicators. This map was all red during the worst of the recession. And the map was all green just just a few months ago.
Now there are a number of red states again.
German Official: "Small concessions are feasible" for Greece
by Calculated Risk on 8/21/2012 08:22:00 AM
From Bloomberg: Germany’s Barthle Says ‘Small Concessions’ Possible for Greece
“Small concessions are feasible provided they are strictly made within the framework of the second aid program,” [Norbert Barthle, the CDU budget spokesman in parliament] said. “For instance, the interest and maturity on loans could be adjusted, as in the case of the first aid package” for Greece. “What’s utterly important is the will of the Greeks to fulfil the terms of financial help. The ball is in the Greeks’ court.”On Friday, Greek Prime Minister Samaras and German Chancellor Merkel will meet in Berlin with a press conference to follow. Europe is about to take center stage once again ...
Monday, August 20, 2012
Research: Loan-to-income guidelines could have "forestalled much of the housing boom"
by Calculated Risk on 8/20/2012 07:34:00 PM
Fed Working Paper by Paolo Gelain, Norges Bank, Kevin Lansing, Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco and Norges Bank, and Caterina Mendicino, Bank of Portugal: House Prices, Credit Growth, and Excess Volatility: Implications for Monetary and Macroprudential Policy
The researchers looked at the house bubble and several possible policy responses. It appears the most effective policy - for limiting the bubble - would have been to require lenders to focus more on loan-to-income.
From the paper:
Our final policy experiment achieves a countercyclical loan-to-value ratio in a novel way by requiring lenders to place a substantial weight on the borrower’s wage income in the borrowing constraint. As the weight on the borrower’s wage income increases, the generalized borrowing constraint takes on more of the characteristics of a loan-to-income constraint. Intuitively, a loan-to-income constraint represents a more prudent lending criterion than a loan-to-value constraint because income, unlike asset value, is less subject to distortions from bubble-like movements in asset prices. Figure 4 [see below] shows that during the U.S. housing boom of the mid-2000s, loan-to-value measures did not signal any significant increase in household leverage because the value of housing assets rose together with liabilities. Only after the collapse of house prices did the loan-to-value measures provide an indication of excessive household leverage. But by then, the over-accumulation of household debt had already occurred. By contrast, the ratio of U.S. household debt to disposable personal income started to rise rapidly about five years earlier, providing regulators with a more timely warning of a potentially dangerous buildup of household leverage.
We show that the generalized borrowing constraint serves as an “automatic stabilizer” by inducing an endogenously countercyclical loan-to-value ratio. In our view, it is much easier and more realistic for regulators to simply mandate a substantial emphasis on the borrowers’ wage income in the lending decision than to expect regulators to frequently adjust the maximum loan-to-value ratio in a systematic way over the business cycle or the financial/credit cycle.
...
... the most successful stabilization policy in our model calls for lending behavior that is basically the opposite of what was observed during U.S. housing boom of the mid-2000s. As the boom progressed, U.S. lenders placed less emphasis on the borrower’s wage income and more emphasis on expected future house prices. So-called “no-doc” and “low-doc” loans became increasingly popular. Loans were approved that could only perform if house prices continued to rise, thereby allowing borrowers to refinance. It retrospect, it seems likely that stricter adherence to prudent loan-to-income guidelines would have forestalled much of the housing boom, such that the subsequent reversal and the resulting financial turmoil would have been less severe.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.From the paper:
Figure 4: During the U.S. housing boom of the mid-2000s, loan-to-value measures did not signal a significant increase in household leverage because the value of housing assets rose together with liabilities. In contrast, the debt-to-income ratio provided a much earlier warning signal of a potentially dangerous buildup of household leverage.Something to remember when the next lending bubble comes along. Also note that debt-to-income is still very high and there is more deleveraging to come.
Leonhardt: Possible Causes of the Income Slump
by Calculated Risk on 8/20/2012 04:55:00 PM
David Leonhardt writes at Economix: The 14 Potential Causes of the Income Slump
Why has median household income just endured its worst 12-year stretch since the Great Depression?Leonhardt has a poll for readers to rank 14 potential causes on why American household income has stagnated including globalization, demographics, fiscal policy, innovation and much more. Leonhardt concludes:
The immediate answer to that question is that economic growth has slowed and inequality has risen. The pie isn’t growing very quickly, and the few new slices are going to a disproportionately small portion of the population.
But that answer is really just an accounting answer. The more important questions are why economic growth has slowed and why inequality has risen – not just over the last 12 years but, less severely, since the early 1970s as well.
In coming days, I’ll be writing posts about what economists see as the major causes.Should be in interesting series.
FNC: Residential Property Values increased 1.1% in June
by Calculated Risk on 8/20/2012 01:42:00 PM
In addition to Case-Shiller, CoreLogic, and LPS, I'm also watching the FNC, Zillow and other house price indexes.
FNC released their June index data today. FNC reported that their Residential Price Index™ (RPI) indicates that U.S. residential property values increased 1.1% in June (Composite 100 index). The other RPIs (10-MSA, 20-MSA, 30-MSA) increased between 1.1% and 1.3% in June. These indexes are not seasonally adjusted (NSA), and are for non-distressed home sales (excluding foreclosure auction sales, REO sales, and short sales).
The year-over-year trends continued to show improvement in June, with the 100-MSA composite down 0.2% compared to June 2011. This is the smallest year-over-year decline in the FNC index since year-over-year prices started declining in 2007 (five years ago).
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
This graph is based on the FNC index (four composites) through June 2012. The FNC indexes are hedonic price indexes using a blend of sold homes and real-time appraisals.
Some of the month-to-month gain is seasonal since this index is NSA. The key is the indexes are showing less of a year-over-year decline in June. If house prices have bottomed, the year-over-year decline should turn positive soon.
The June Case-Shiller index will be released Tuesday, August 28th.
Mortgage Cramdowns: A Missed Opportunity
by Calculated Risk on 8/20/2012 11:20:00 AM
Binyamin Appelbaum at the NY Times reviews some of the Obama administration's missed opportunities: Cautious Moves on Foreclosures Haunting Obama
Here is an excerpt on mortgage cramdowns:
Former Representative Jim Marshall, a centrist Georgia Democrat who lost his House seat in 2010, was a staunch advocate of the administration’s economic policies. He supported the banking bailout. He opposed a similar bailout for homeowners.Both Tanta and I urged changing the bankruptcy laws to allow mortgage cramdowns. Here was a piece from Tanta in 2007 (yes, 2007) explaining mortgage cramdowns and why they were the appropriate policy: Just Say Yes To Cram Downs (For new readers, Tanta was my former co-blogger and mortgage banker. You can read about her here).
The administration made just one mistake, he said in a recent interview: it failed to rewrite the bankruptcy code.
Congressional Democrats wanted to change the law to permit “cramdown” — a term that meant letting bankruptcy courts cut mortgage debts — to put pressure on mortgage companies to modify loans and to provide a backup plan for borrowers who could not get the help they needed.
“There was another way to deal with this, and that is what I supported: forcing the banks to deal with this,” Mr. Marshall said. “It would have been better for the economy and lots of different neighborhoods and people owning houses in those neighborhoods.”
Mr. Obama sponsored cramdown legislation as a senator, endorsed it as a presidential candidate and called on Congress to pass it in the Arizona speech.
But he also repeatedly pressed the pause button. When proponents sought to add a cramdown to the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act in September 2008, Mr. Obama, who had flown back to Washington from the campaign trail, persuaded them to postpone the “partisan” effort as an example to Republicans, who said the measure would violate existing contracts.
In February 2009, after Mr. Obama became president, the White House asked Democrats not to attach the measure to the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, fearing it would cost votes. In March, a watered-down version finally passed the House, but the mortgage industry rallied opposition to block it in the Senate.
Some officials said the White House had tried and failed. But other officials and participants, including Mr. Marshall, said it simply was not a priority.
“There wasn’t enough political capital, time or energy,” said Mr. Barr, the former Treasury deputy.
Cramdowns in bankruptcy are still an appropriate policy, and hopefully the candidates will be asked in the debates about what policies they will pursue to help the unemployed and to address foreclosures - and be asked specifically about cramdowns.


